The article emphasizes the essential steps for successfully planting and caring for East Indian Mango trees. It offers detailed guidance on:
- Optimal growing conditions
- Planting techniques
- Maintenance practices
- Troubleshooting common issues
Key factors such as sunlight, soil quality, and proper watering are highlighted as critical for healthy fruit production. By following these guidelines, gardeners can ensure robust growth and fruitful yields.
🥭 Thinking about growing a Mango Tree in your garden?
Explore the East Indian Mango Tree at Everglades Farm - shipped directly from Florida.
Introduction
Cultivating the East Indian mango tree can transform any garden into a tropical paradise, providing not only lush greenery but also the promise of sweet, succulent fruit. This guide outlines the essential steps for planting and caring for these magnificent trees, ensuring they thrive in their ideal warm, sunny environments. Many aspiring gardeners may wonder about the key factors that can influence the success of their mango cultivation. Understanding the nuances of soil, water, and pest management is crucial for overcoming common challenges and reaping a bountiful harvest.
1. Understand the Growing Conditions for East Indian Mango Trees
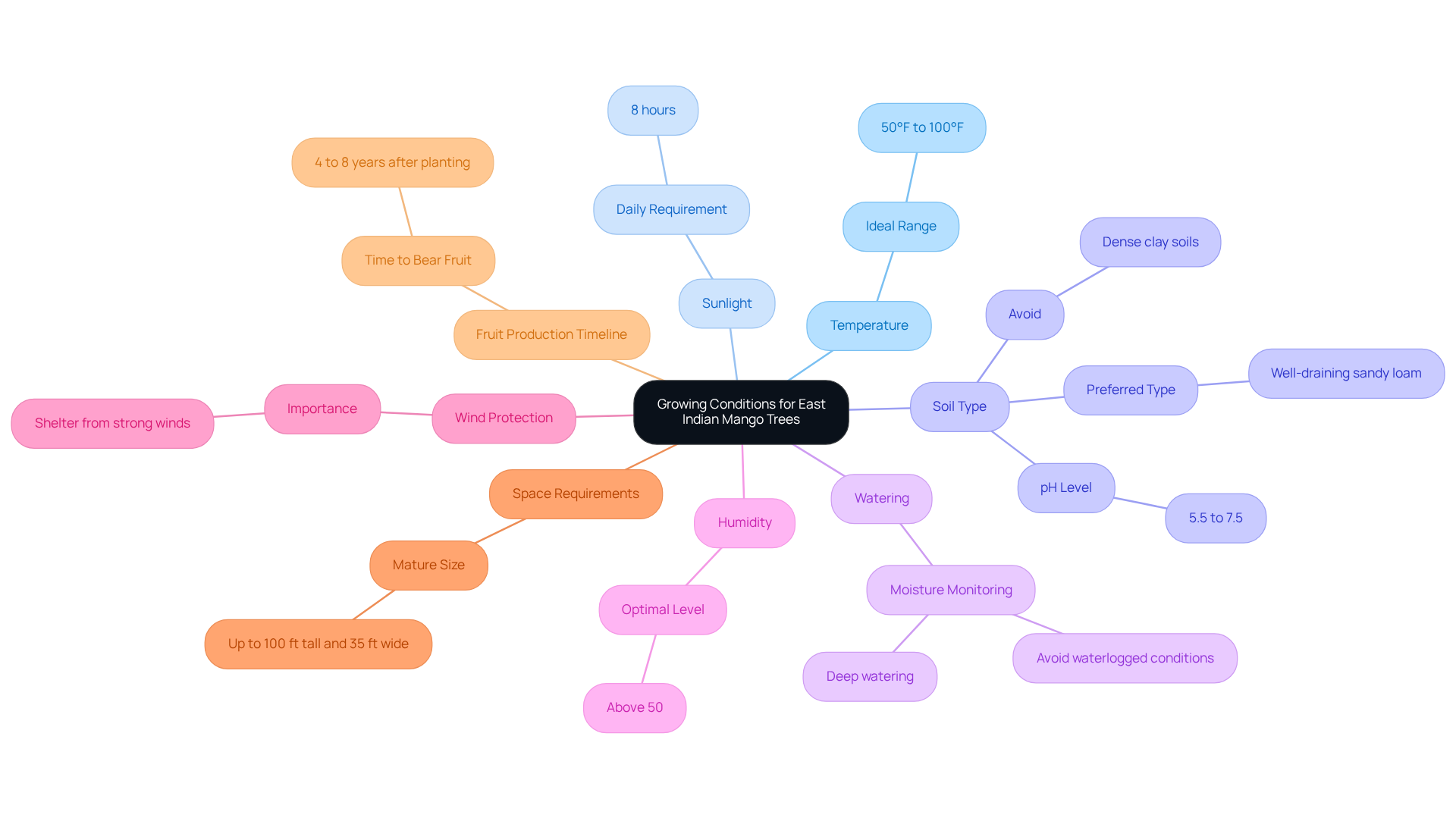
East Indian Mango trees flourish in warm, tropical climates, ideally thriving within a temperature range of 50°F to 100°F. They require complete sunlight for at least eight hours each day to produce healthy fruit. The preferred soil type is well-draining sandy loam, with a pH level between 5.5 and 7.5; dense clay soils should be avoided as they retain water, increasing the risk of root rot. Selecting a planting location that offers shelter from strong winds is crucial, as these can damage both the plant and its fruit.
Regular monitoring of soil moisture is essential, as these plants prosper with deep watering but should not be allowed to remain in waterlogged conditions. Furthermore, mango plants thrive in humidity levels above 50 percent for optimal growth. For gardeners in cooler climates, it is important to bring potted mango plants indoors before temperatures fall below 50°F. These trees can grow to heights of up to 100 ft. and widths of 35 ft., making it vital to plan for adequate space.
With proper care, the East Indian Mango tree typically begins to produce fruit approximately 4 to 8 years after planting. By adhering to these guidelines, gardeners can significantly enhance the successful cultivation of the East Indian mango tree in tropical environments.
2. Plant Your East Indian Mango Tree: Step-by-Step Instructions
-
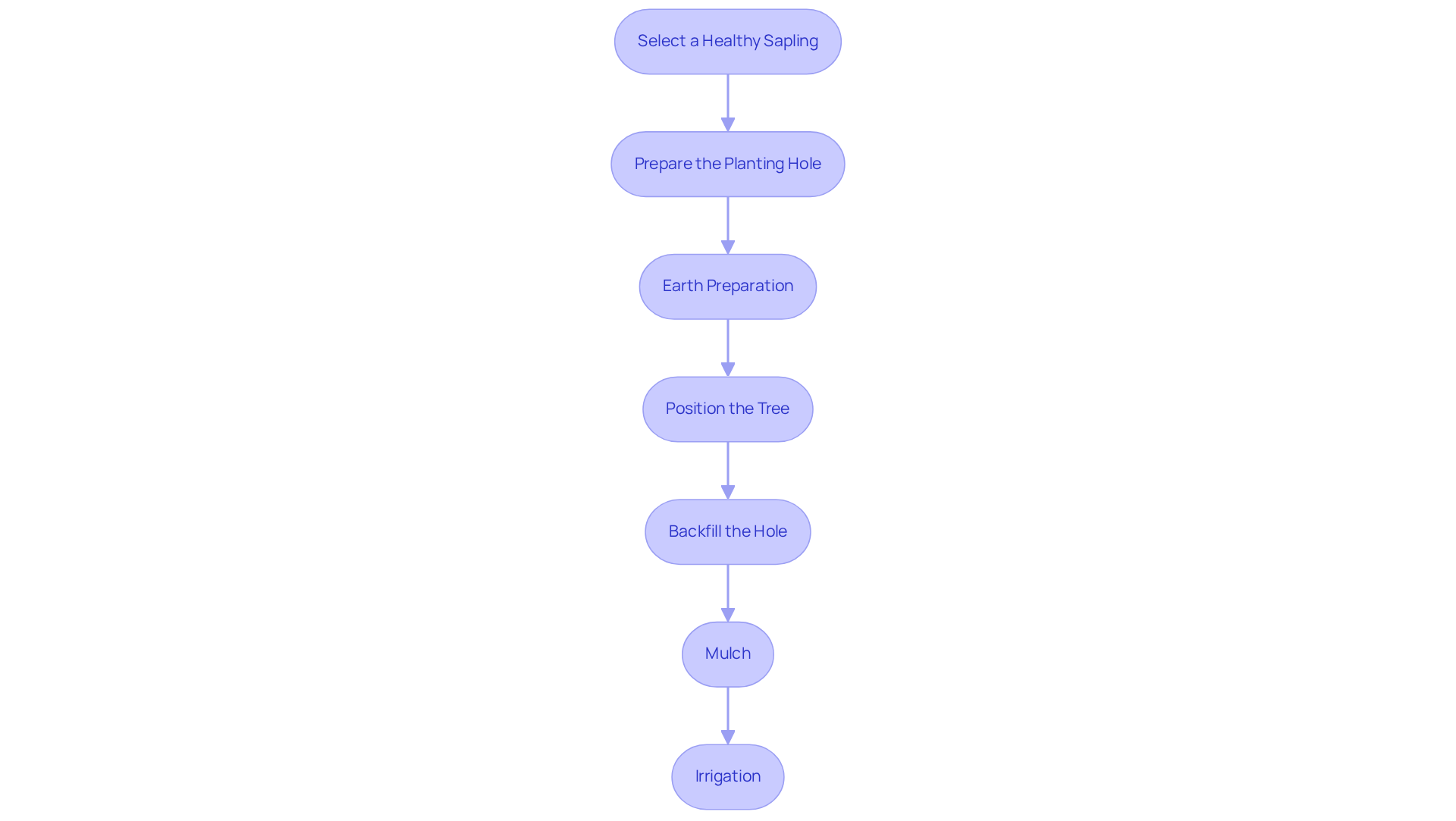
Select a healthy sapling by choosing a grafted East Indian Mango tree from a reputable nursery, ensuring it has a strong stem and healthy leaves. This selection is crucial for the plant's establishment and future growth.
-
Prepare the Planting Hole: Dig a hole that is twice as wide and as deep as the root ball of the sapling. This preparation allows for proper root expansion, which is essential for the tree's health.
-
Earth Preparation: Combine the excavated material with compost to improve nutrient content and drainage, creating a rich environment for the roots. Additionally, for those interested in cultivating passion fruit or soursop, adding organic matter can further enhance ground structure and fertility, benefiting all tropical plants.
-
Position the Tree: Place the sapling in the center of the hole, ensuring that the top of the root ball is level with the surrounding ground. Avoid planting too deep. When planting soursop trees, ensure they are spaced adequately to accommodate their larger canopy, promoting healthy growth.
-
Backfill the Hole: Fill the hole with the prepared earth mixture, gently tamping it down to remove air pockets. Water the area thoroughly to settle the soil, ensuring a stable environment for the roots.
-
Mulch: Apply a layer of organic mulch around the base of the plant to retain moisture and suppress weeds. This practice is especially advantageous for soursop plants, which thrive in well-mulched environments, enhancing their growth potential.
-
Irrigation: Provide the plant with ample water after planting and maintain a damp environment without excess moisture for the initial weeks as the roots develop. For passion fruit vines, consistent hydration is essential during their early growth stages to encourage healthy development.
3. Maintain Your Mango Tree: Care and Maintenance Tips
-
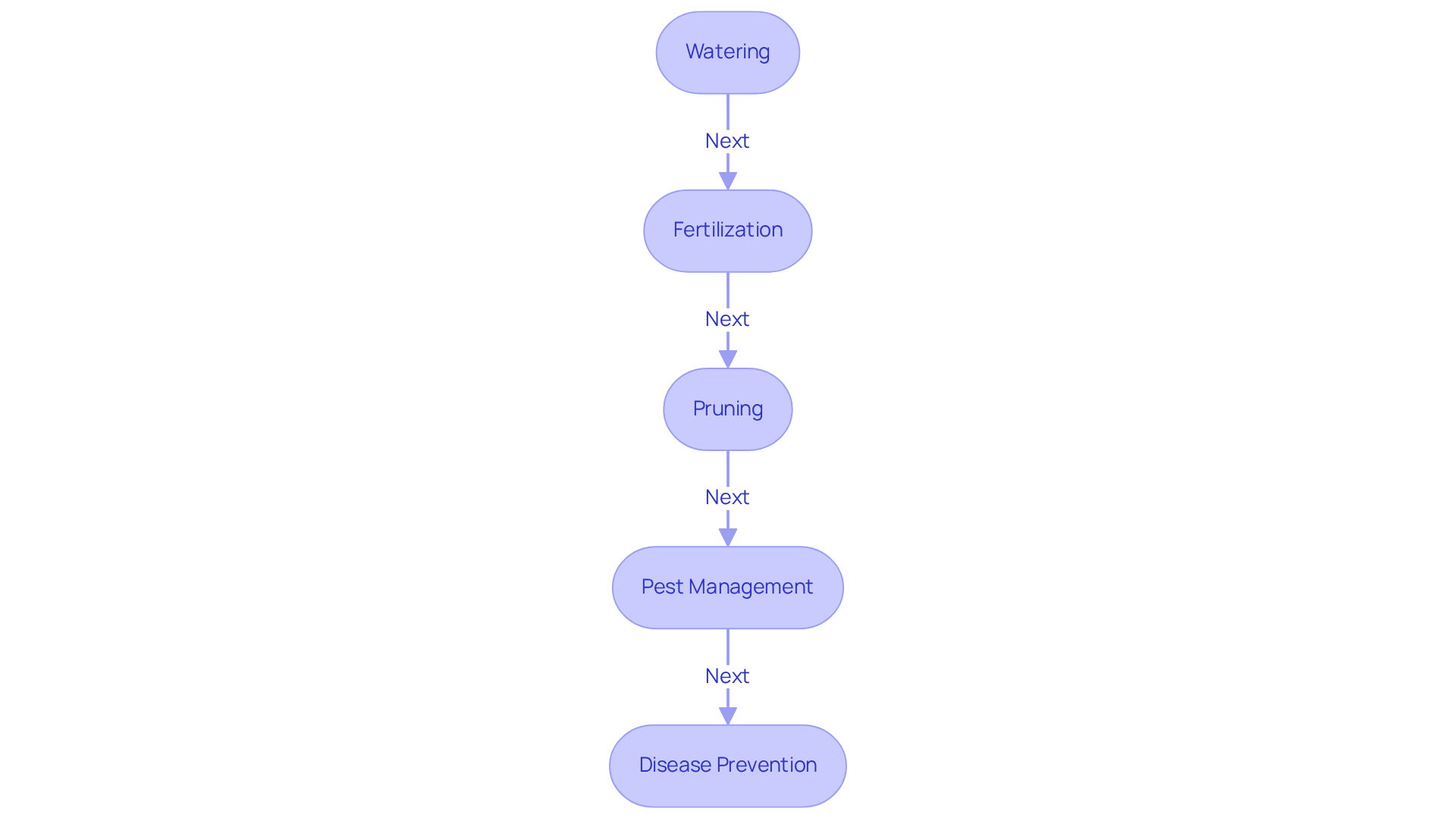
Watering: For optimal growth, it is essential to irrigate mango plants thoroughly but infrequently, allowing the top inch of soil to dry out between waterings. During dry periods, increase the frequency to ensure the tree receives sufficient hydration. Mature mango plants typically require irrigation every 10-14 days, while young plants need watering every 1-2 weeks, particularly in arid conditions to establish their root systems. Adjusting the watering frequency according to precipitation and soil moisture levels is crucial. Implementing a strategic phase of water stress for 50-60 days can enhance yield during blooming, resulting in higher annual output and reduced water consumption. Regular soil moisture checks are vital to prevent both over-irrigation and insufficient watering, which can negatively impact plant health.
-
Fertilization: Apply a balanced fertilizer specifically designed for tree crops every 6-8 weeks during the growing season, which spans from spring to early fall. This schedule fosters healthy growth and optimizes yield. Incorporating organic and slow-release fertilizers can further enhance soil health and yield, promoting sustainable practices in mango cultivation.
-
Pruning: Conduct annual pruning to remove dead or diseased branches and shape the canopy. This practice encourages better air circulation and sunlight penetration, both of which are vital for fruit development.
-
Pest Management: Regularly inspect your mango plant for pests such as aphids and mealybugs. If infestations occur, manage them using organic insecticidal soap or neem oil, which are effective and environmentally friendly options.
-
Disease Prevention: Ensure good air circulation around the plant and avoid overhead watering to reduce the risk of fungal diseases. Promptly address any signs of illness with appropriate fungicides to maintain plant health.
4. Troubleshoot Common Issues in Mango Tree Cultivation
-
Leaf Yellowing: Yellowing leaves often signal nutrient deficiencies, particularly nitrogen, magnesium, or iron. To address this, check the soil pH and consider applying a nitrogen-rich fertilizer, such as Macrofert 20:20:20 at 5 gm/lit, which supports vegetative growth and amino acid formation. Additionally, for magnesium deficiency, applying Magmix at 4-5 gm/lit is recommended, and for iron deficiency, use Chelafer at 1-2 gm/lit.
-
Poor Yield: If your mango plant blossoms but does not develop produce, insufficient pollination or nutrient shortages, especially phosphorus, might be the causes. Ensure the tree is positioned in a location with good airflow and adequate sunlight to enhance pollination success. Applying phosphorus-rich fertilizers can further support flowering and fruiting.
-
Produce Drop: Excessive produce drop can result from water stress or nutrient deficiencies. Maintaining consistent watering and fertilization practices, especially during flowering, is crucial to support the retention and development of produce. Mulching can also help stabilize soil moisture during this critical period.
-
Pest Infestations: Regularly check for pests such as flies or scale insects. Implementing integrated pest management strategies, including cultural controls, traps, or organic pesticides, can effectively control these populations and safeguard your mango plant.
-
Fungal Diseases: The appearance of black spots on leaves or fruit may indicate anthracnose, while powdery mildew can appear as a white powdery coating. Promptly remove affected parts and apply a suitable fungicide as needed. Additionally, ensuring proper spacing between trees promotes air circulation, reducing the risk of fungal infections.
Conclusion
Mastering the cultivation of East Indian mango trees involves understanding their specific growing conditions, proper planting techniques, and ongoing care. By ensuring these trees are planted in the right climate, receiving adequate sunlight, and provided with well-draining soil, gardeners can create an environment conducive to healthy growth and fruitful yields.
Key insights from this guide highlight the importance of:
- Selecting a healthy sapling
- Preparing the planting hole correctly
- Maintaining optimal watering and fertilization practices
Additionally, regular monitoring for pests and diseases, along with implementing effective pruning techniques, can significantly enhance the health and productivity of the mango tree. Promptly addressing common issues such as leaf yellowing, poor yields, and pest infestations will further ensure the success of your mango cultivation efforts.
In conclusion, cultivating East Indian mango trees is a rewarding endeavor that requires attention to detail and a commitment to best practices. By following the outlined steps and maintaining vigilance against potential challenges, gardeners can enjoy the sweet rewards of their labor. Embrace the journey of growing your mango tree and contribute to a sustainable gardening practice that nourishes the body and enriches the soul.
Grow Your Own Tropical Paradise with East Indian Mango Trees!
Start now and enjoy the sweet rewards of your gardening efforts with premium trees from Everglades Farm.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the ideal growing conditions for East Indian Mango trees?
East Indian Mango trees thrive in warm, tropical climates with temperatures ranging from 50°F to 100°F, require at least eight hours of full sunlight daily, and prefer well-draining sandy loam soil with a pH level between 5.5 and 7.5.
How much sunlight do East Indian Mango trees need?
They need complete sunlight for at least eight hours each day to produce healthy fruit.
What type of soil is best for East Indian Mango trees?
The preferred soil type is well-draining sandy loam, and dense clay soils should be avoided as they retain water and increase the risk of root rot.
How should I protect East Indian Mango trees from environmental factors?
It is important to select a planting location that offers shelter from strong winds, as these can damage both the plant and its fruit.
How often should I water East Indian Mango trees?
Regular monitoring of soil moisture is essential; these plants prosper with deep watering but should not remain in waterlogged conditions.
What humidity levels are optimal for East Indian Mango tree growth?
Mango plants thrive in humidity levels above 50 percent for optimal growth.
What should I do with potted mango plants in cooler climates?
In cooler climates, it is important to bring potted mango plants indoors before temperatures fall below 50°F.
How large can East Indian Mango trees grow?
East Indian Mango trees can grow up to 100 ft. in height and 35 ft. in width, making it vital to plan for adequate space.
When can I expect East Indian Mango trees to start producing fruit?
With proper care, East Indian Mango trees typically begin to produce fruit approximately 4 to 8 years after planting.





0 comments