The Boston fern, characterized by its lush, arching fronds and tropical charm, is a popular choice for indoor gardeners looking to introduce a vibrant touch of greenery to their homes. However, caring for this delicate plant necessitates a comprehensive understanding of its specific needs, including humidity levels and soil composition. When the vibrant leaves begin to wilt or turn brown, it raises concerns about the plant's health. This guide explores essential care practices for Boston ferns, providing insights and solutions to ensure these stunning plants not only survive but flourish in their indoor environments.
🌱 Thinking of growing a Boston Fern plant?
Explore Boston Fern Plant at Everglades Farm - shipped directly from Florida.
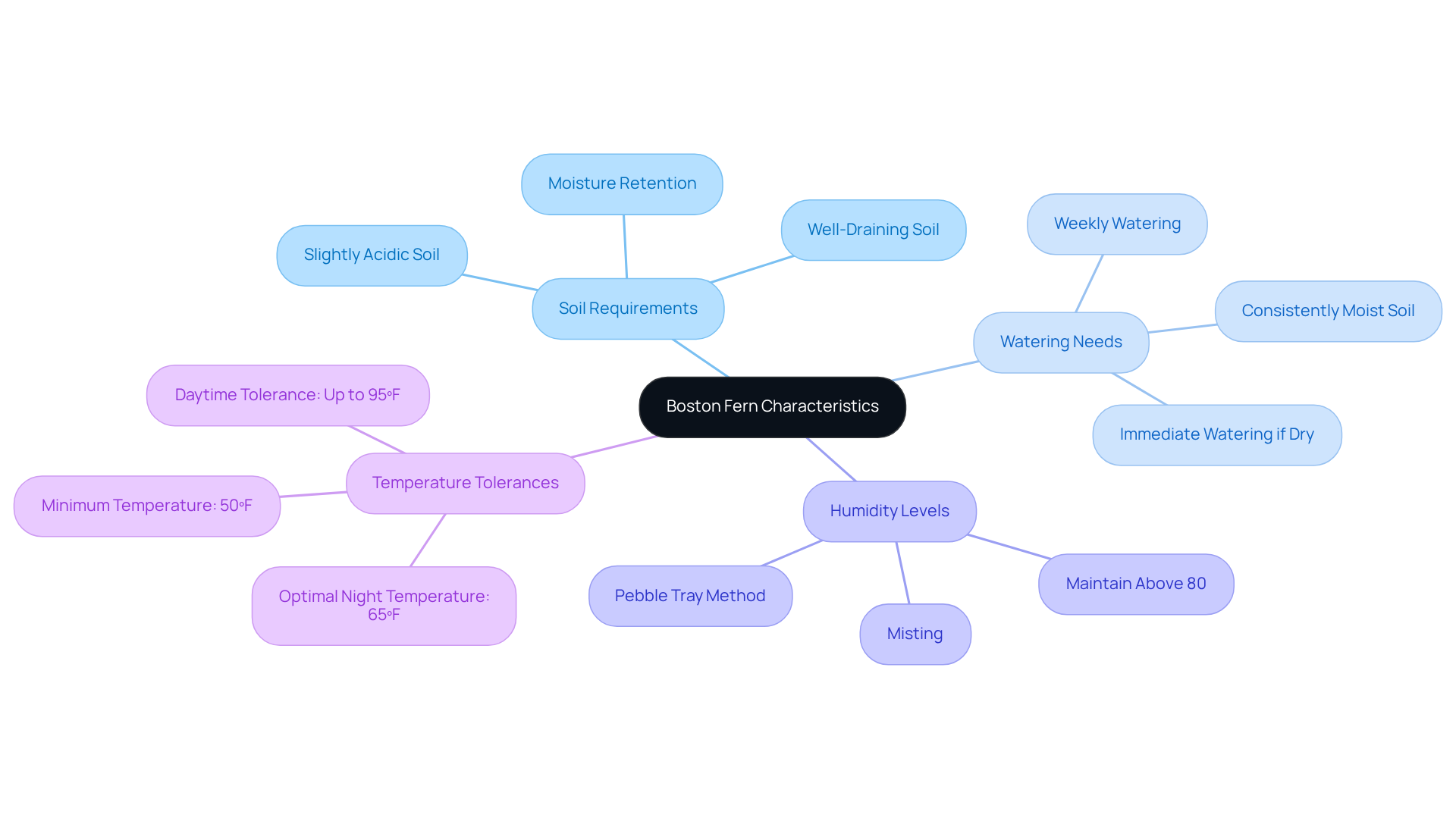
Understand Boston Fern Characteristics
- Slightly acidic, well-draining soil that retains moisture without becoming waterlogged.
- Regular watering; the soil should remain consistently moist, and it is advisable to water the plant weekly, particularly when the upper layer of soil feels dry.
- Maintaining humidity levels; when relative humidity drops below 80%, misting the plant or placing it on a tray of damp pebbles can help create a more favorable environment.
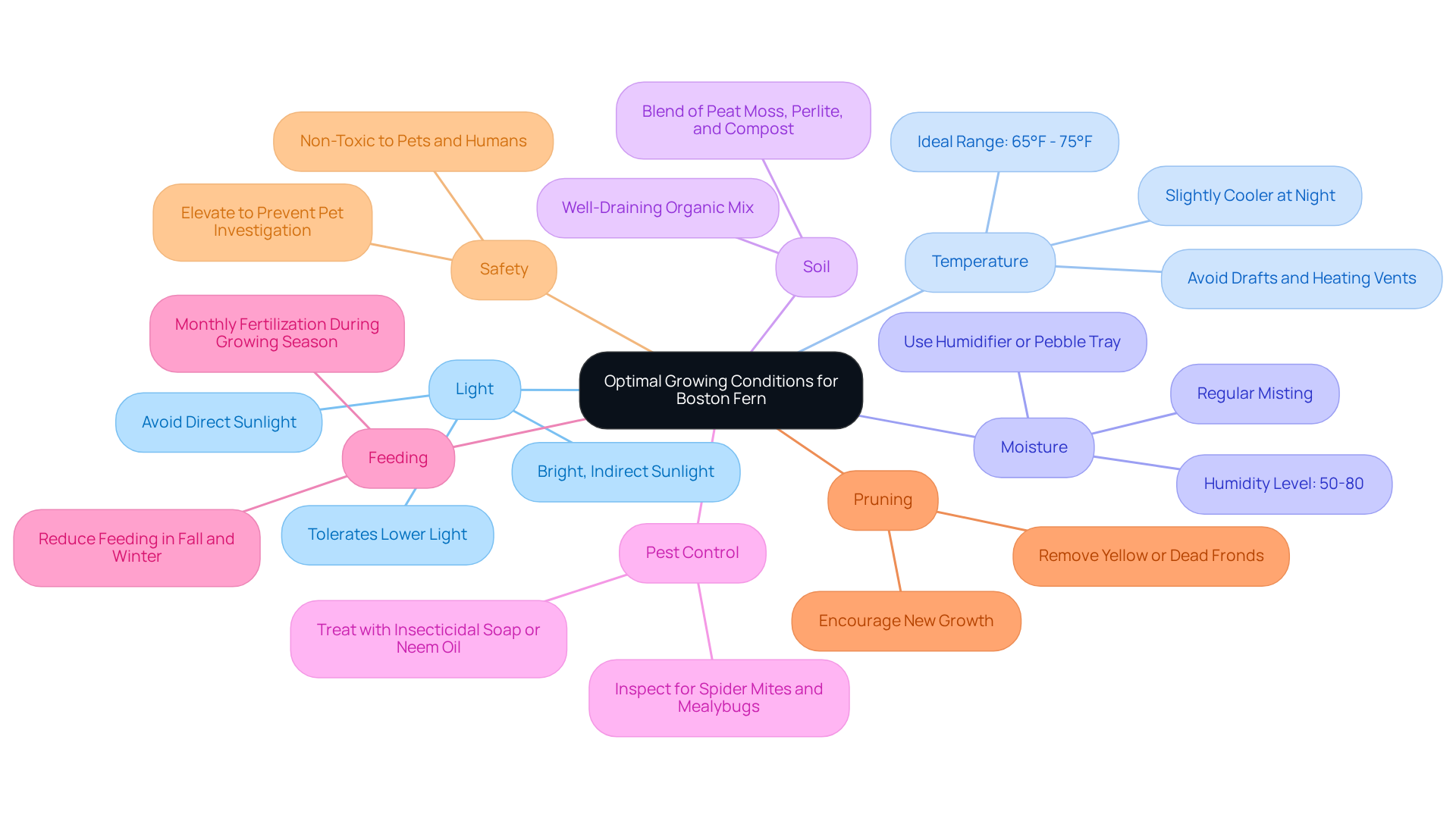
2. Establish Optimal Growing Conditions
- Light: Place your plant in a location that receives bright, indirect sunlight. Direct sunlight can scorch the delicate fronds, so a location near a north or east-facing window is ideal for maintaining lush growth.
- Temperature: Keep the temperature between 65°F and 75°F during the day, with slightly cooler conditions at night. Avoid positioning the plant close to drafts or heating vents, as temperature variations can strain it.
- Moisture: Ferns thrive in elevated moisture levels, ideally between 50-80%. To increase moisture, utilize a humidifier, set the pot on a tray filled with pebbles and water, or mist the fronds regularly to create a suitable environment. Be aware that brown tips on certain ferns can signify low humidity or insufficient watering, so monitor moisture levels closely.
- Soil: Opt for a well-draining, organic potting mix that retains moisture without becoming soggy. A blend of peat moss, perlite, and compost is effective for supporting healthy root development and moisture retention.
- Pest Control: Regularly inspect for typical pests such as spider mites and mealybugs, which can impact the Boston fern plant. If detected, treat them promptly with insecticidal soap or neem oil.
- Feeding: Reduce feeding during the fall and winter months when the plant's growth slows down to prevent nutrient buildup.
- Pruning: Prune any yellow, dead, or damaged fronds as they appear to encourage new growth and maintain a lush appearance.
- Safety: These plants are non-toxic to pets and humans, making them a secure option for homes with children or animals.
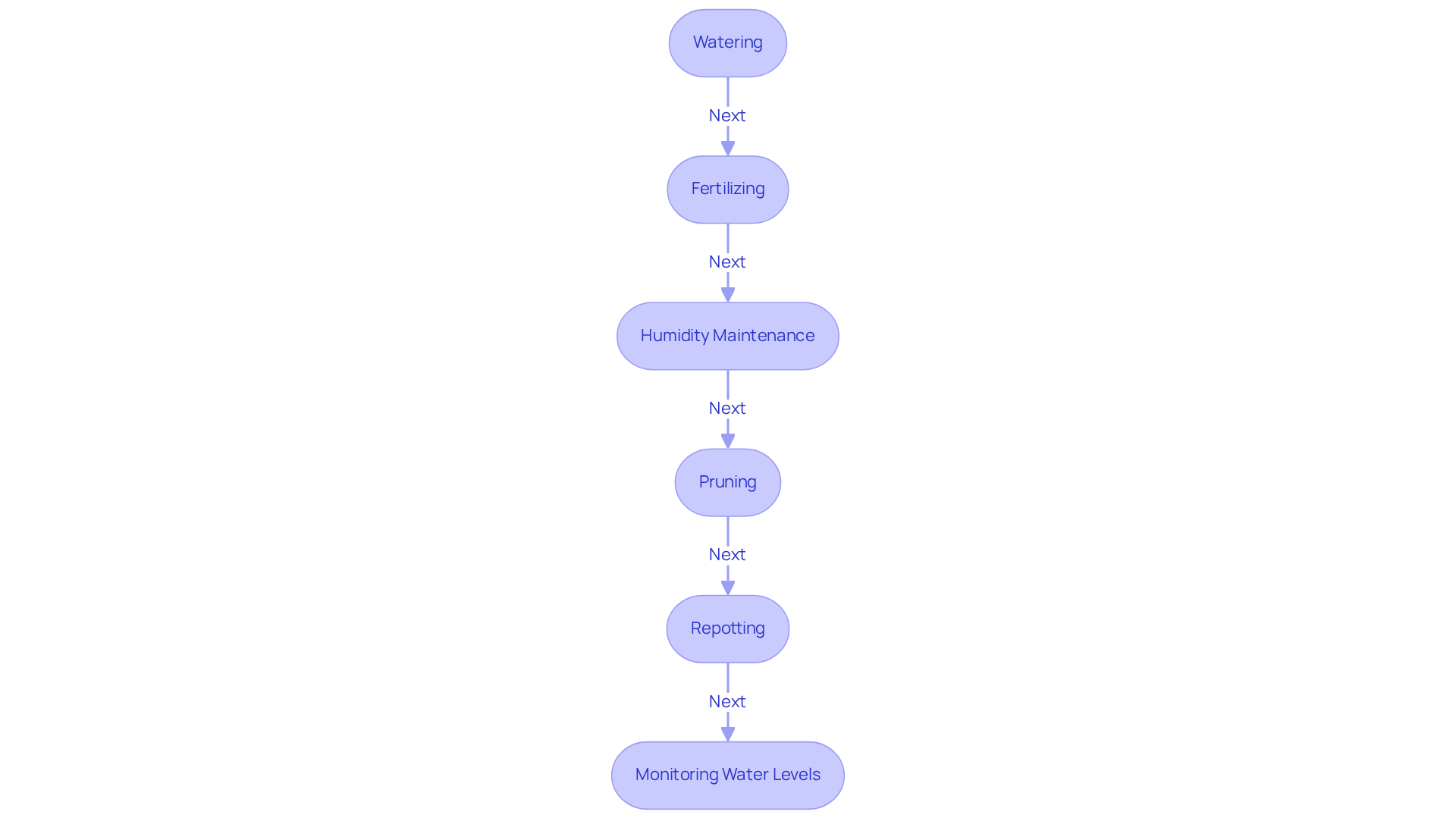
3. Implement Care and Maintenance Practices
-
Water your plant thoroughly when the top inch of soil feels dry. During the growing season (spring and summer), these plants generally require watering every 2-3 days. In contrast, during fall and winter, they need watering every 4-7 days. The boston fern plant flourishes in consistently damp soil, but it is crucial to prevent overwatering, which can lead to root decay. Using filtered or distilled water is recommended to avoid chemical buildup from tap water that can harm the plant. Employing a bottom-watering technique can help maintain moisture levels without wetting the fronds directly.
-
Fertilizing is another key aspect of care. During the growing season (spring and summer), fertilize your plant every 4-6 weeks with a diluted liquid fertilizer. A balanced fertilizer with an NPK ratio of 20-10-20 is ideal for promoting healthy growth. For indoor plants, this schedule remains consistent, ensuring they receive the necessary nutrients for vibrant foliage.
-
The boston fern plant thrives in humidity levels between 50% and 80%. Frequent spraying of the leaves can assist in maintaining these humidity levels, particularly in arid indoor settings, enhancing the plant's overall health.
-
Pruning is essential for promoting new growth. Regularly eliminate any dead or yellowing leaves to enhance the plant's appearance and prevent disease by improving air circulation around the foliage.
-
Repotting should occur every 1-2 years or when the plant becomes root-bound. Select a pot that is one size larger and refresh the soil to provide essential nutrients, ensuring the plant has ample space to grow and flourish.
-
Lastly, be aware of the signs of overwatering and underwatering. Symptoms of overwatering include yellowing leaves and droopy foliage, indicating potential root rot. Conversely, underwatering can result in dry, crispy leaves and wilting, signaling a need for additional water.
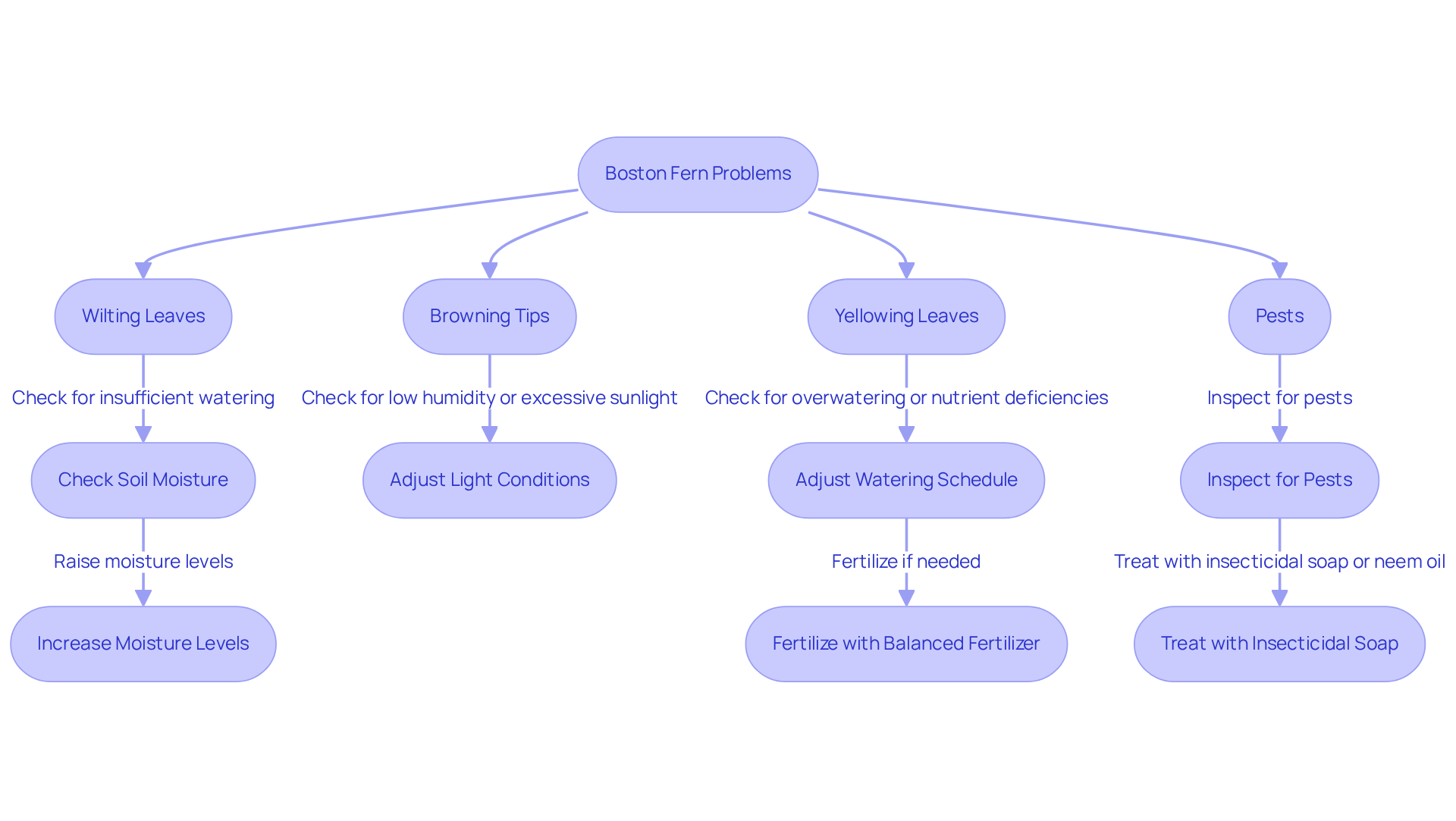
4. Troubleshoot Common Boston Fern Problems
-
Browning Tips: Browning tips on leaves can suggest low humidity or excessive direct sunlight. Direct sunlight can damage Boston plant leaves, resulting in browning and loss of texture. Ensure the plant is positioned in an appropriate spot with bright, indirect illumination to avoid leaf damage.
-
Yellowing Leaves: Yellowing leaves can result from overwatering or nutrient deficiencies. Overwatering can cause root rot, which is characterized by a foul smell and blackened roots. Adjust your watering schedule to keep the soil evenly moist but not soggy, and consider fertilizing with a balanced liquid fertilizer during the growing season.
-
Pests: Common pests include mealybugs and spider mites. Regularly inspect the undersides of fronds and treat infestations with insecticidal soap or neem oil. Soil drenches with insecticides are a more effective control method for pests. Maintaining humidity through regular misting can also deter pests and promote a healthier environment for your plant.
5. Additional Care Tips for Boston Ferns
-
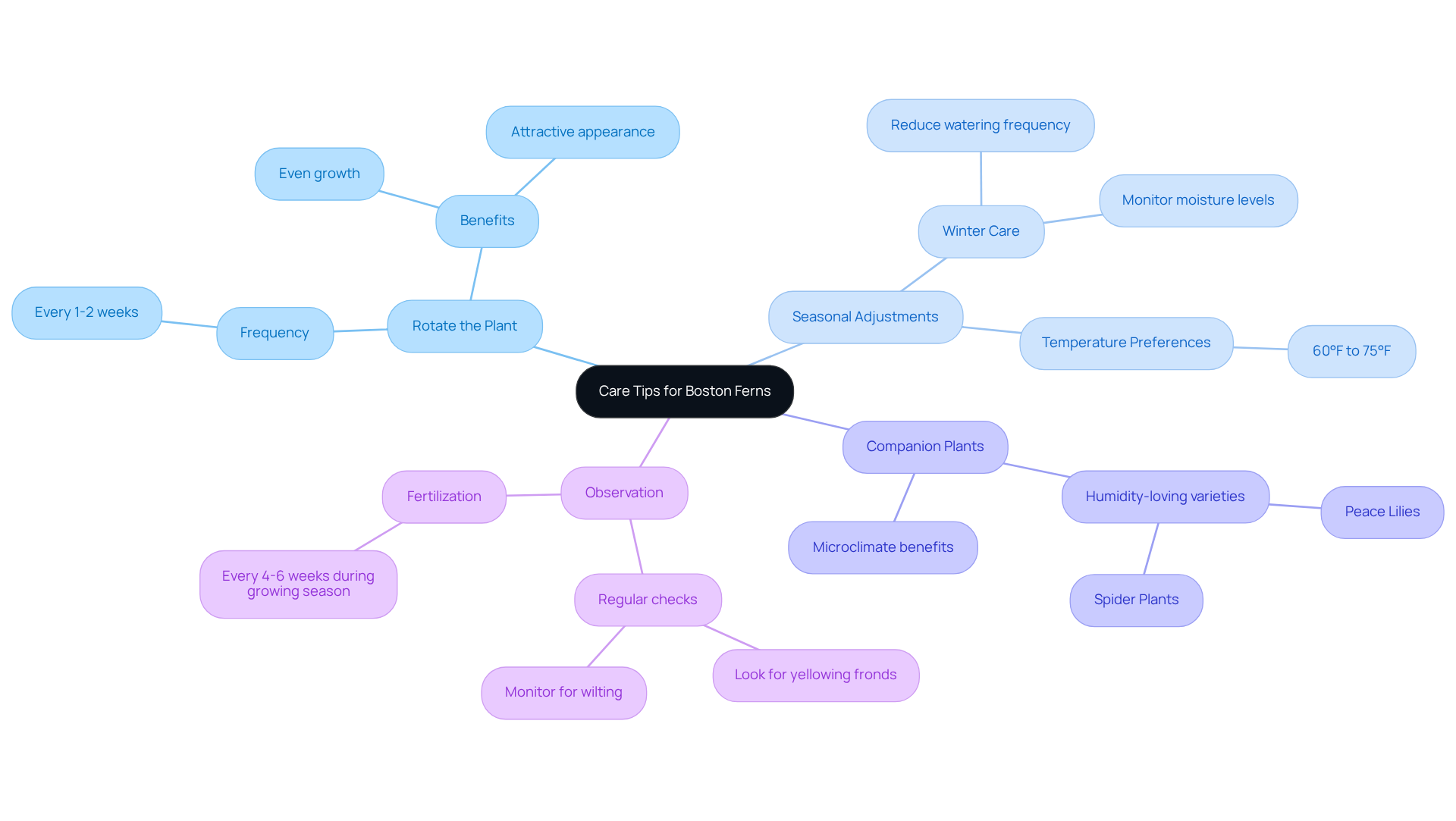
Rotate the Plant: To promote even growth, rotate your houseplant every 1-2 weeks. This practice ensures that all sides receive adequate light exposure, preventing uneven growth. Gardening expert Reese L. Robins emphasizes that this method helps maintain an attractive and well-balanced appearance indoors.
-
Seasonal Adjustments: In winter, reduce watering frequency as the plant's growth slows. It is crucial to monitor moisture levels carefully, particularly in warm indoor environments, to avoid stress. The Boston fern plant flourishes in conditions where humidity levels are no less than 50% and prefers consistent temperatures ranging from 60°F to 75°F.
-
Companion Plants: Position your Boston fern plant next to other humidity-loving varieties, such as peace lilies or spider plants. This arrangement creates a microclimate that enhances moisture levels, benefiting all plants involved.
-
Observation: Regularly check your plant for any changes in appearance. Early detection of issues like yellowing fronds or wilting can significantly improve recovery chances and overall health. Additionally, fertilize your Boston fern plant every 4-6 weeks during the growing season, from spring through summer, to replenish nutrients in the soil.
Conclusion
- Optimal growing conditions
- Watering practices
- Pest management
- Troubleshooting common issues
🌱Transform Your Space with Lush Boston Ferns!
Frequently Asked Questions





0 comments