
Understanding Blue Agave: Origins, Uses, and Importance
Share
Blue agave, scientifically recognized as Agave tequilana plays a crucial role in the production of tequila, serves as a cultural symbol, and contributes ecologically, particularly within Mexico.
This article highlights its economic significance, noting that the tequila industry generates substantial revenue. Additionally, it underscores the importance of adopting sustainable farming practices to mitigate biodiversity concerns that arise from intensive cultivation methods.
Thinking about growing an agave in your garden?
Explore Blue Agave at Everglades Farm - shipped directly from Florida.
Define Blue Agave: Characteristics and Significance
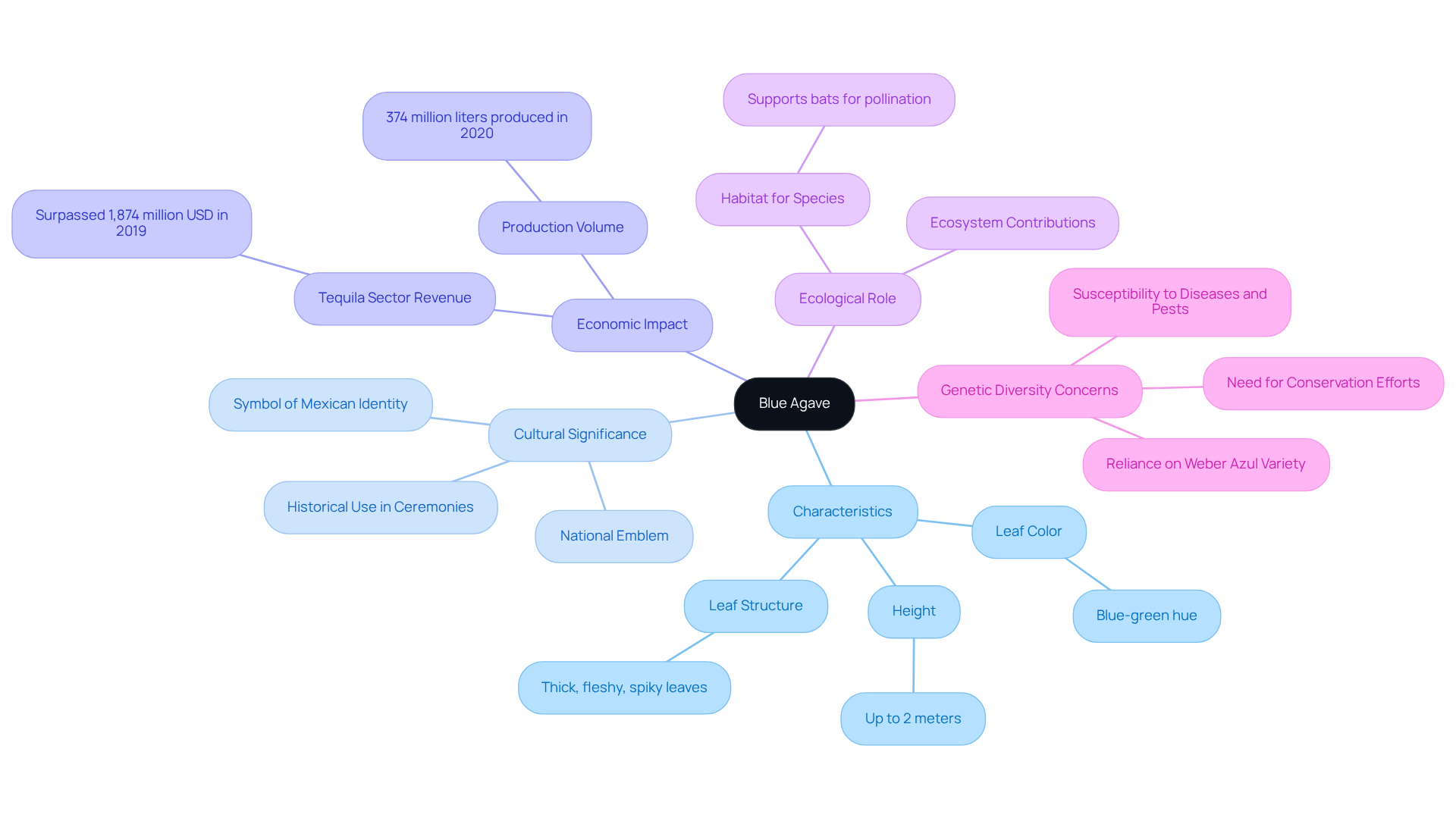
Blue agave, which is scientifically recognized as Agave tequilana, is a succulent species that originates from Mexico and particularly thrives in the Jalisco region. This remarkable plant features a rosette of thick, fleshy, spiky leaves, which can reach and display a striking blue-green hue.
Beyond its primary role in spirit production, the blue agave also serves as a powerful symbol of Mexican culture and identity, embodying the rich traditions and heritage of the region. The high sugar content of blue agave, predominantly in the form of fructose, makes it exceptionally suitable for fermentation and distillation, thereby solidifying its significance in the beverage industry.
In 2019, the tequila sector revenue surpassed 1,874 million USD, emphasizing the economic impact of azure plant cultivation. Additionally, the blue agave is vital in local ecosystems, providing essential habitat and sustenance for various species, including bats, which are crucial for its pollination.
The cultural significance of the blue agave species is further highlighted by its historical use in indigenous ceremonies and its recognition as a national emblem, illustrating the profound connection between the organism and the Mexican population.
However, reliance on the Weber Azul variety raises concerns about genetic diversity, making it more susceptible to diseases and pests. As specialists note, 'The genetic diversity of the plant is under threat due to reliance on the Weber Azul variety for tequila production,' underscoring the urgent need for conservation efforts.
Explore the Origins and Cultural Importance of Blue Agave
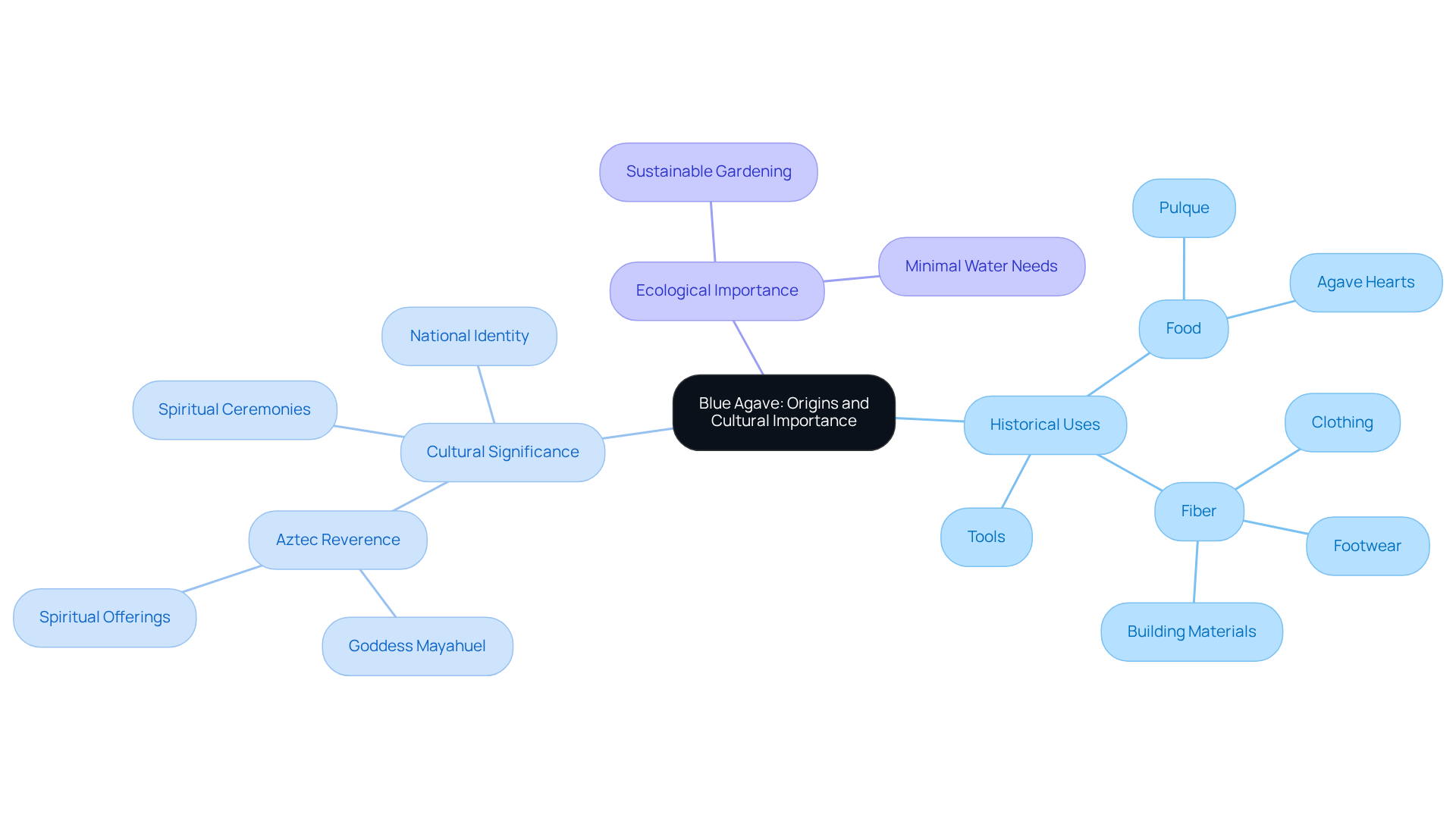
The origins of blue species date back thousands of years to the native peoples of Mesoamerica, who utilized the plant for various essential purposes, including food, fiber, tools, and alcoholic beverages. The Aztecs esteemed the plant, associating it with the goddess Mayahuel, a symbol of fertility and nourishment. The fermentation of sap from this plant into pulque, a traditional alcoholic drink, played a pivotal role in religious ceremonies and social gatherings, with spiritual leaders consuming it to foster communication with the divine.
Upon the , the potential for distillation was recognized, leading to the production of spirits. Today, the blue plant serves not only as a vital ingredient in spirit production but also as a cultural emblem, celebrated in festivals and regarded as a significant aspect of Mexico's national identity.
Furthermore, the ecological importance of the blue succulent is considerable; it requires minimal water and flourishes in poor soil conditions, making it an ideal candidate for sustainable gardening practices.
Examine the Uses of Blue Agave in Food and Beverage Production
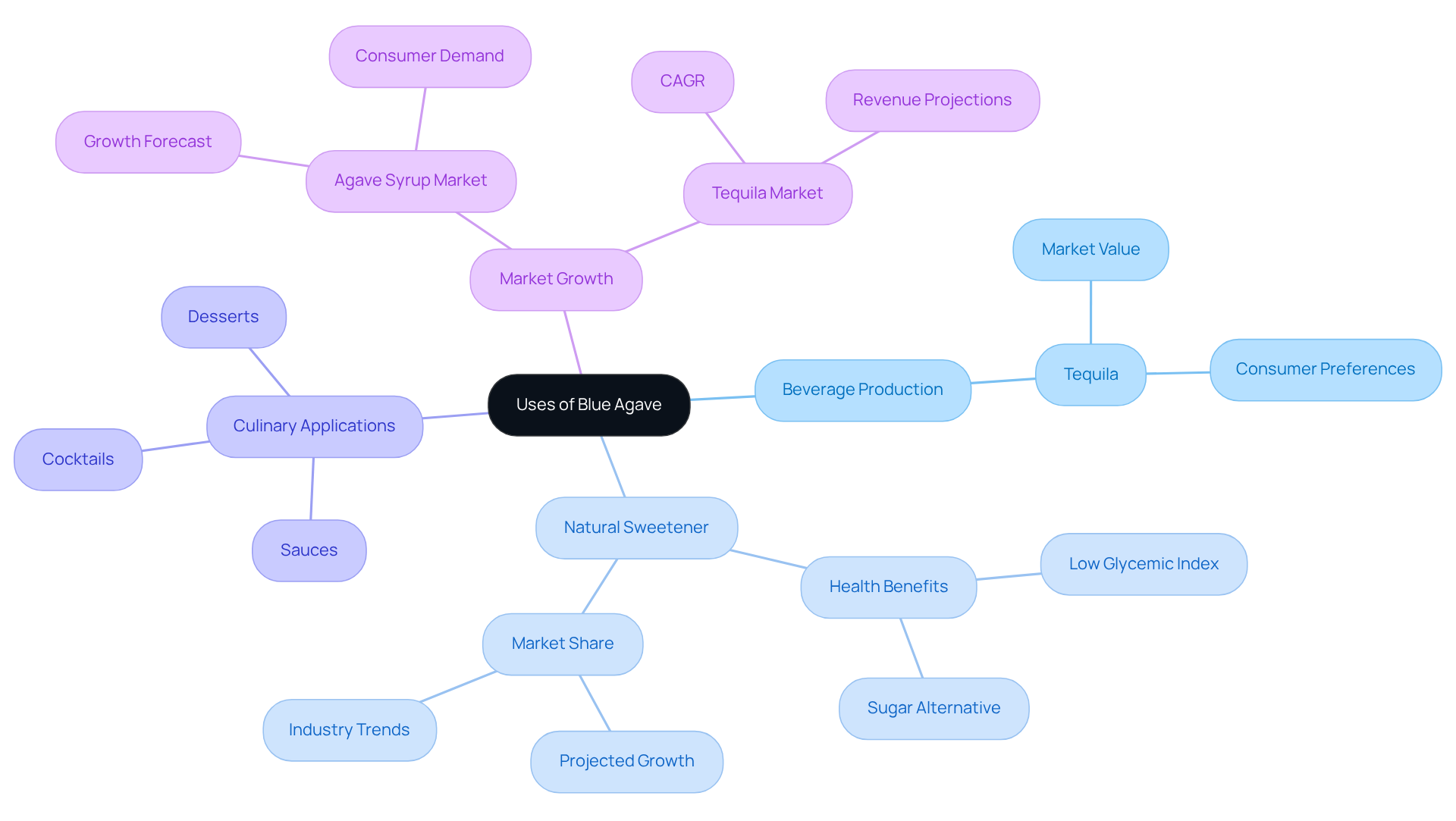
The production of a globally recognized distilled spirit is primarily associated with blue agave. The process commences with the harvesting of the plant's heart, or piña, which is cooked to transform its starches into fermentable sugars. Following fermentation, the liquid undergoes distillation to yield tequila.
Additionally, the blue agave plant is utilized to create syrup, which serves as a natural sweetener that has gained traction in the food industry as a healthier alternative to sugar. Its low glycemic index appeals to individuals aiming to regulate their blood sugar levels.
Beyond beverages, the blue agave plant finds applications in various culinary creations, including sauces, desserts, and cocktails, showcasing its versatility in contemporary gastronomy.
The market for syrup derived from blue agave is expected to experience significant growth, with forecasts suggesting an increase from USD 645 million in 2025 to USD 1,233.6 million by 2035, indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.7%. This expansion is fueled by a rising consumer preference for and the growing popularity of plant-based diets.
Furthermore, the light sweetener derived from cactus plants is expected to capture a 60% share of the industry by 2025, underscoring its importance in the market. Brands are innovating to satisfy this demand, with companies like Wholesome Sweeteners and Nature's Way incorporating syrup made from blue agave into their product offerings, aligning with the trend of health-conscious baking.
As awareness of the syrup's health advantages continues to proliferate, its uses in food and beverage production are anticipated to broaden, solidifying its status as a staple ingredient in kitchens around the globe.
Assess the Ecological and Economic Impact of Blue Agave Cultivation
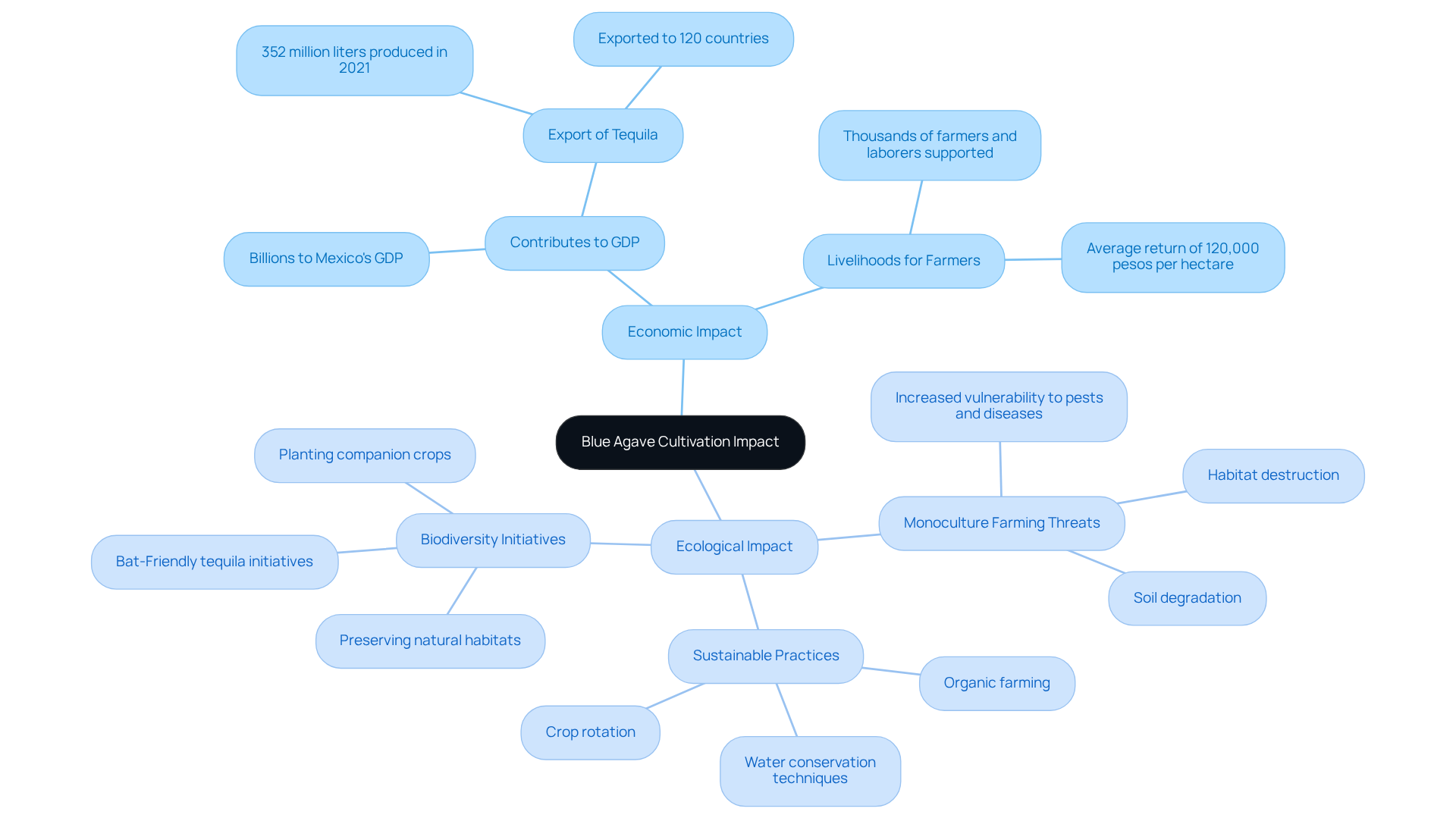
The cultivation of blue agave has significant ecological and economic implications. Economically, the agave spirits sector contributes billions to Mexico's GDP, providing livelihoods for thousands of farmers and laborers. However, the rising demand for tequila has resulted in that threaten biodiversity and soil health.
- Large-scale monoculture farming often leads to habitat destruction and increased vulnerability to pests and diseases.
- To mitigate these effects and ensure the long-term viability of the cultivation of blue agave, sustainable methods such as crop rotation and organic farming are crucial.
- Furthermore, initiatives aimed at promoting biodiversity—like planting companion crops and preserving natural habitats—can enhance the resilience of agave farming while supporting local ecosystems.
Conclusion
The blue agave plant, scientifically known as Agave tequilana, serves as a vital component of Mexico's cultural identity and plays a significant role in the global beverage industry. Its unique features, such as striking blue-green leaves and high sugar content, make it an essential ingredient in the production of tequila and various culinary delights. This remarkable plant not only embodies the rich traditions of Mexican heritage but also contributes to local economies and ecosystems.
Key insights throughout the article reveal the multifaceted roles of blue agave, from its historical significance among indigenous peoples to its contemporary applications in food and beverage production. The economic impact of blue agave cultivation is considerable, with the tequila sector generating billions in revenue and providing livelihoods for many individuals. However, challenges posed by intensive farming practices underscore the urgent need for sustainable agricultural methods to preserve both the plant's genetic diversity and the health of local ecosystems.
Given the blue agave's importance, it is imperative for consumers and producers to advocate for sustainable practices that protect this iconic plant and its environment. By recognizing the interconnectedness of cultural heritage, economic viability, and ecological health, a collective effort can ensure that blue agave continues to thrive for generations to come. Embracing sustainable agriculture not only honors the rich history of blue agave but also secures its future as a cornerstone of Mexican identity and global culinary innovation.
Cultivate Your Own Slice of Paradise with Tropical Trees
Join Everglades Farm in nurturing sustainable gardens that celebrate nature’s bounty—start growing today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is blue agave and where does it originate?
Blue agave, scientifically known as Agave tequilana, is a succulent species that originates from Mexico, particularly thriving in the Jalisco region.
What are the physical characteristics of blue agave?
Blue agave features a rosette of thick, fleshy, spiky leaves that can reach heights of up to 2 meters and display a striking blue-green hue.
What role does blue agave play in the beverage industry?
Blue agave has a high sugar content, mainly in the form of fructose, making it exceptionally suitable for fermentation and distillation, which is crucial for spirit production, particularly tequila.
How significant is the tequila sector economically?
In 2019, the tequila sector revenue surpassed 1,874 million USD, highlighting the economic impact of blue agave cultivation.
What ecological role does blue agave serve?
Blue agave is vital in local ecosystems, providing essential habitat and sustenance for various species, including bats, which are crucial for its pollination.
What cultural significance does blue agave hold in Mexico?
Blue agave embodies rich traditions and heritage, having historical use in indigenous ceremonies and being recognized as a national emblem, illustrating its profound connection to the Mexican population.
What concerns exist regarding the genetic diversity of blue agave?
The reliance on the Weber Azul variety for tequila production raises concerns about genetic diversity, making the plant more susceptible to diseases and pests, which underscores the urgent need for conservation efforts.


