
Sapodilla Tree Growing Zone
Share
Understanding the specific growing zones for sapodilla trees is crucial for any aspiring gardener aiming to cultivate this tropical fruit. These trees thrive in warm climates, and it is essential for potential growers to assess local conditions to ensure successful growth and fruit production.
Choosing the wrong growing zone can lead to various challenges, such as poor growth rates and reduced fruit yield. Therefore, gardeners must navigate these complexities effectively to maximize their sapodilla yields.
Understand Growing Zones for Sapodilla Trees
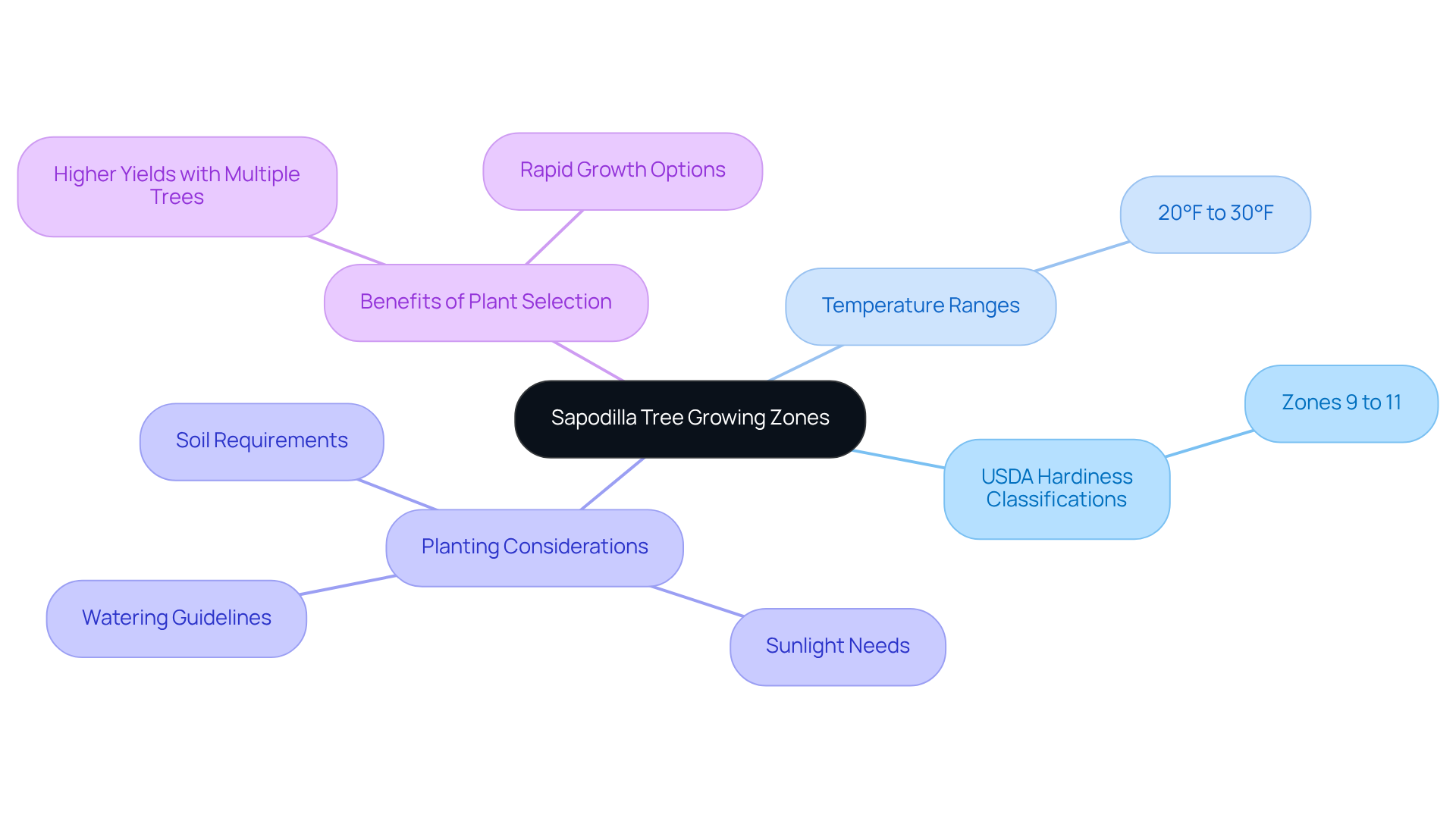
Growing regions are defined geographical areas that reflect specific climate conditions, particularly temperature ranges. For chico fruit plants, understanding the USDA hardiness classifications is essential, as these plants flourish in areas 9 to 11, where temperatures generally vary from 20°F to 30°F for Area 9, with slight frost.
Comprehending your expanding area is crucial for determining if your local climate is suitable for planting this particular fruit within the sapodilla tree growing zone. To find your zone, consult the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, which categorizes regions based on their average annual minimum temperatures. This knowledge ensures that your fruit-bearing plant will thrive in your garden, as these plants require warm climates and can be sensitive to cold snaps.
Furthermore, these fruit-bearing plants may take three or more years before producing a yield; they are self-fertile but generate greater harvests when situated near other plants. By selecting tropical plants from Everglades Farm's Fast-Growing Trees collection, home gardeners can enjoy the benefits of high-yield species designed for rapid gardening success.
Horticulturists emphasize that selecting the right sapodilla tree growing zone is essential for successfully raising tropical fruit plants, as it ensures they receive the warmth and conditions necessary for optimal growth.
Assess Your Local Climate Conditions
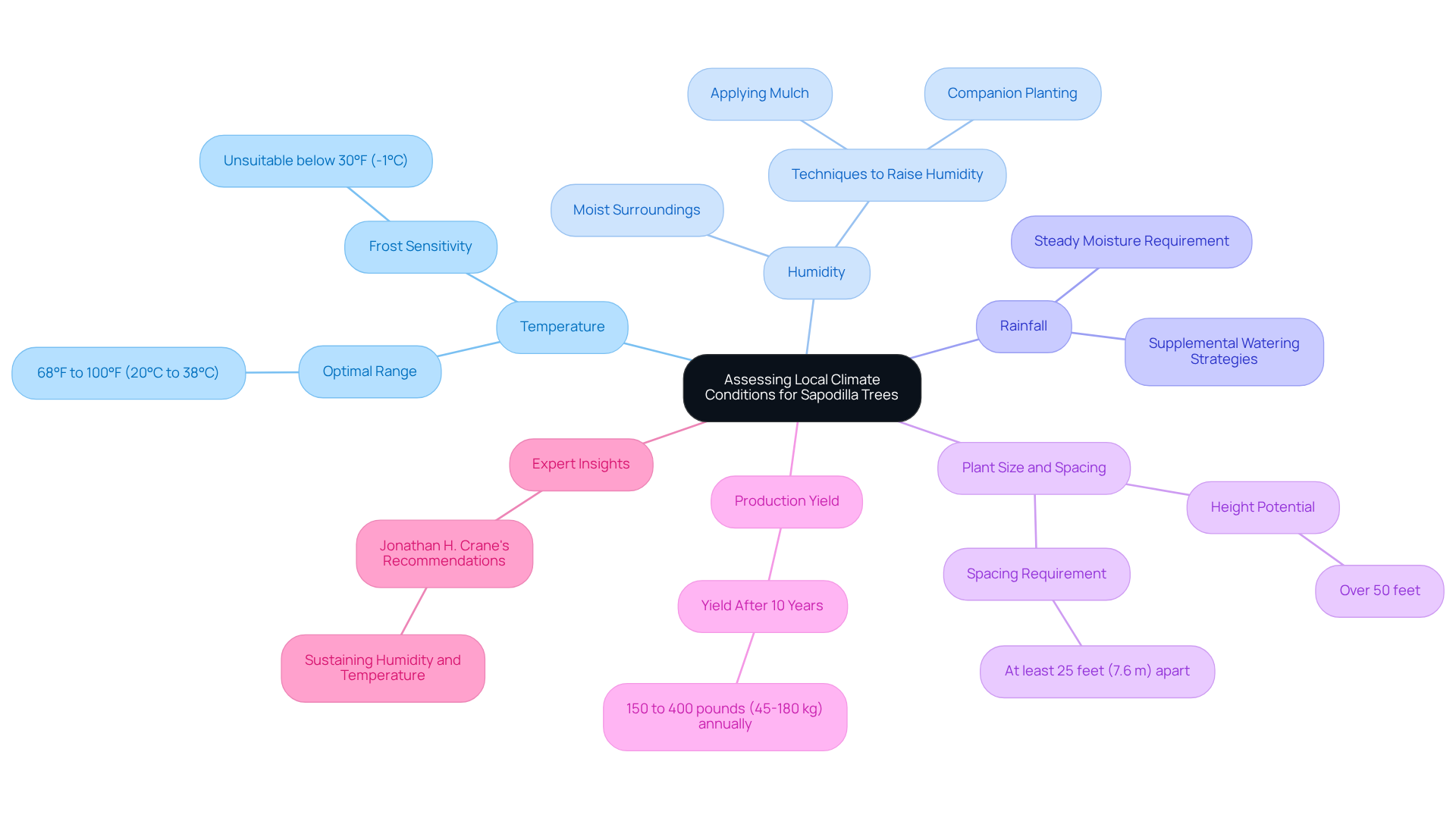
To effectively assess your local climate conditions for growing sapodilla trees, it is crucial to consider several key factors:
-
Temperature: Sapodilla plants flourish in temperatures ranging from 68°F to 100°F (20°C to 38°C). They are particularly sensitive to frost, making regions that experience temperatures below 30°F (-1°C) less suitable for their growth. Understanding this temperature range is vital for ensuring the health of your sapodilla tree growing zone.
-
Humidity: These plants thrive in moist surroundings, which are essential for their overall well-being and fruit yield. In drier regions, raising humidity around the plant can be advantageous. Techniques such as applying mulch to retain moisture or planting companion plants that naturally enhance humidity levels can create a more favorable microclimate for sapodilla growth in the sapodilla tree growing zone.
-
Rainfall: Steady moisture is crucial for these plants, particularly throughout their growth period. Ensure that your area receives adequate rainfall or be prepared to implement supplemental watering strategies to maintain soil moisture, which is vital for healthy development in the sapodilla tree growing zone.
-
Plant Size and Spacing: Sapodilla plants can reach heights of over 50 feet, so it is essential to position them at least 25 feet (7.6 m) away from other plants or structures. This spacing helps avoid shading and ensures optimal growth and fruit production, maximizing the plant's potential.
-
Production Yield: After approximately 10 years, a well-tended fruit-bearing plant can produce between 150 to 400 pounds (45-180 kg) of fruit annually. This significant yield makes sapodilla trees a beneficial addition to your garden in the sapodilla tree growing zone, providing both beauty and bounty.
-
Expert Insights: As stated by Jonathan H. Crane, a professor and specialist in tropical fruit crops, sustaining the appropriate humidity and temperature is essential for the successful development of tropical fruit plants such as sapodilla. His insights underline the importance of these climatic factors in nurturing healthy plants.
By thoroughly assessing these climatic factors, you can gain valuable insights into how well this particular fruit plant will flourish in your garden, particularly within the sapodilla tree growing zone, ultimately leading to a more fruitful and vibrant cultivation experience.
Determine Your Growing Zone Using Resources
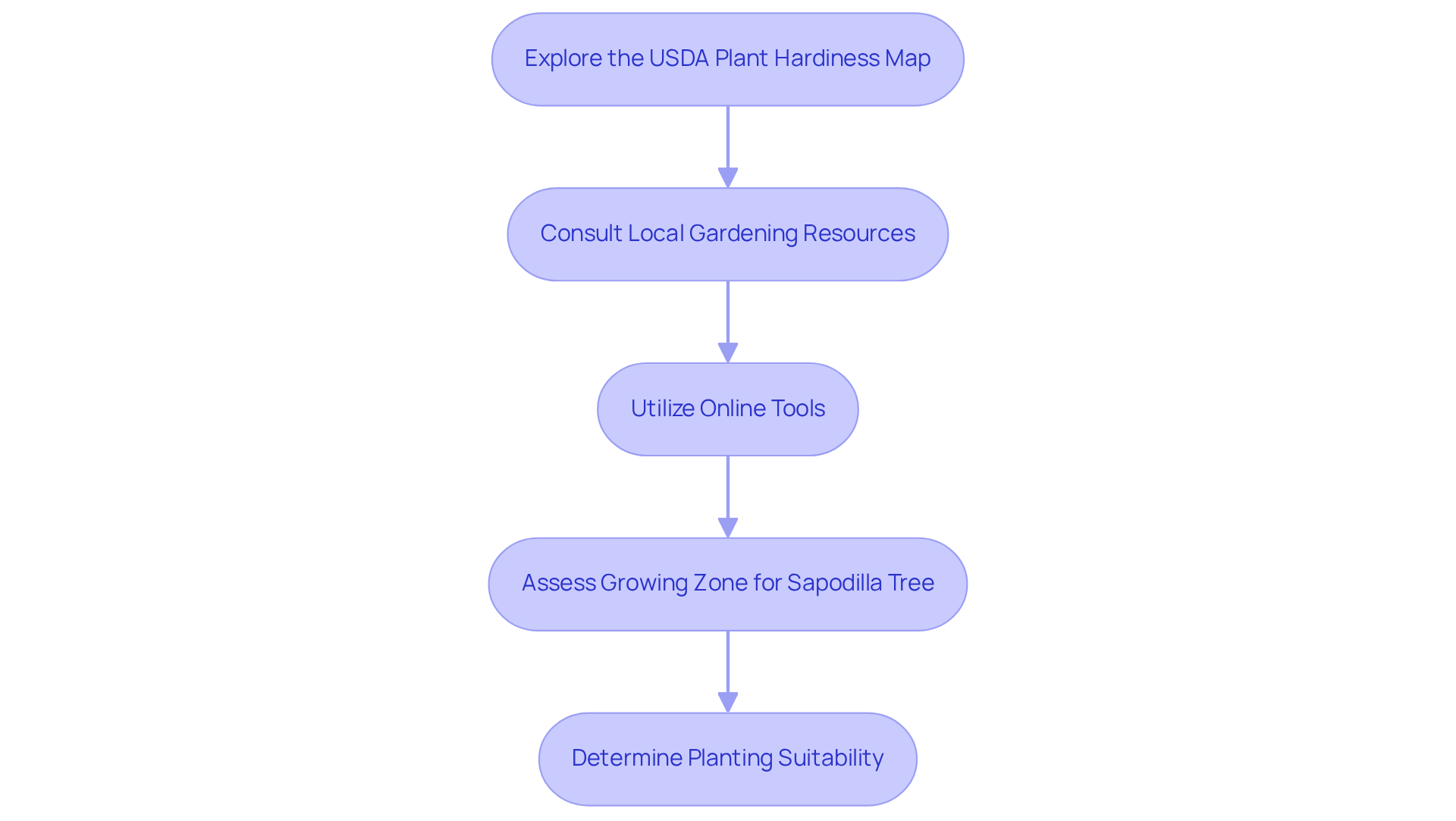
To determine your growing zone for planting a sapodilla tree, follow these essential steps:
-
Explore the USDA Plant Hardiness Map: This interactive resource allows you to input your zip code, providing specific information about your cultivation area based on average annual extreme minimum winter temperatures. Dr. Simon Liu, ARS Administrator, states, "These updates reflect our ongoing commitment to ensuring the Plant Hardiness Zone Map remains a premier source of information that gardeners, growers, and researchers alike can use."
-
Consult Local Gardening Resources: Reach out to local extension services or gardening centers, which often offer tailored information regarding cultivation areas specific to your region. The National Wildlife Federation underscores the importance of leveraging local resources to promote climate-smart gardening practices.
-
Utilize Online Tools: Websites such as the Arbor Day Foundation and American Meadows provide lookup tools that assist in determining your gardening area based on location, simplifying the selection of suitable plants. With the 2023 map indicating that approximately half of the U.S. has transitioned to the next warmer half zone, it is essential to utilize updated resources to ensure your gardening choices align with current conditions.
By following these steps, you can confidently assess whether this fruit-bearing plant will thrive in your garden, especially if it is located in the sapodilla tree growing zone, thereby enhancing your home gardening experience.
Consider Challenges and Best Practices for Your Zone
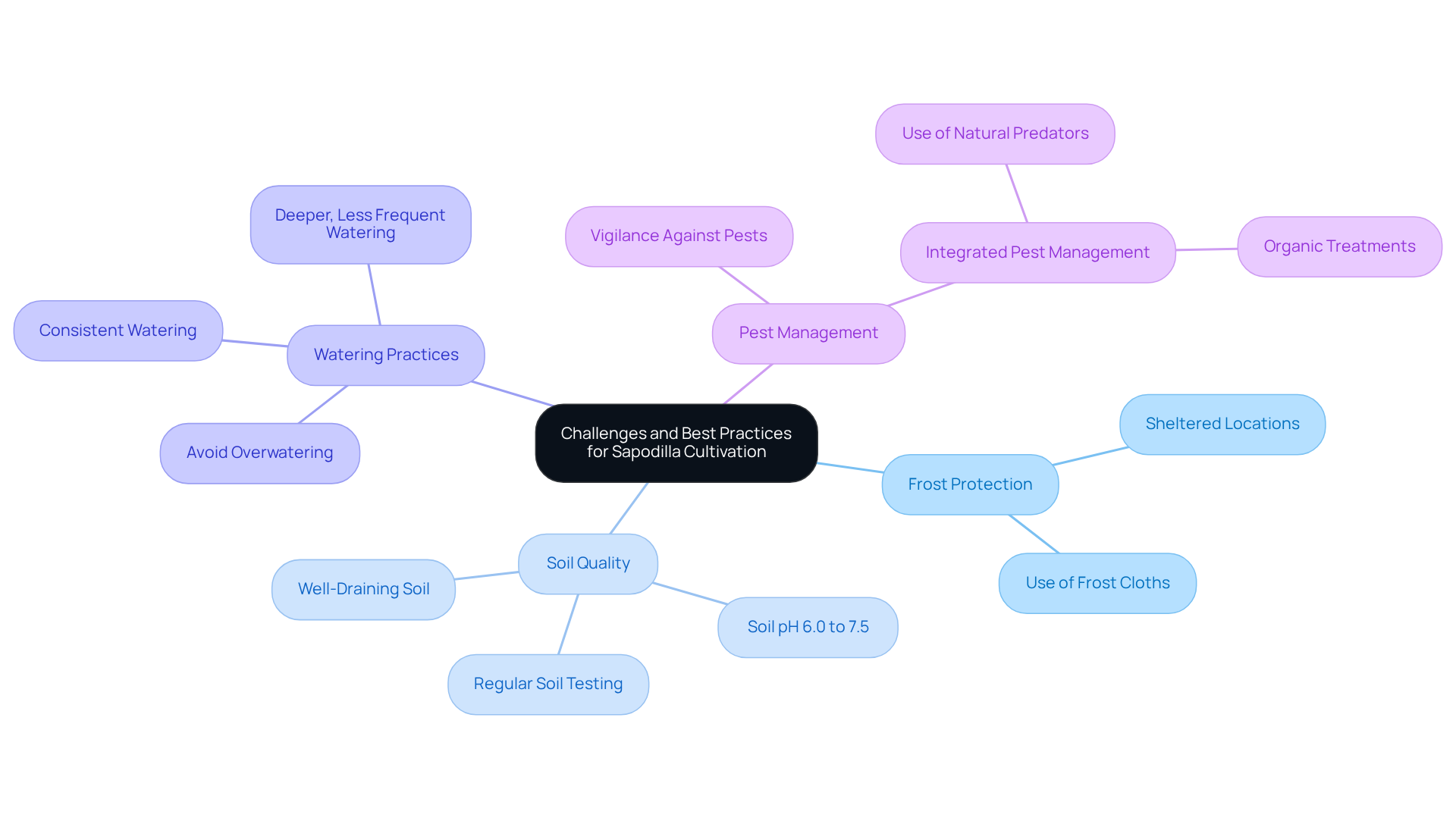
When cultivating sapodilla trees, it is essential to address specific challenges and adopt best practices that are tailored to your sapodilla tree growing zone.
-
Frost Protection: In frost-prone areas, it is crucial to position sapodilla plants in sheltered locations or utilize frost cloths during cold spells to safeguard them from potential harm. This proactive approach helps ensure the plants' survival and encourages healthy growth.
-
Soil Quality: Prioritizing well-draining soil enriched with organic matter is key. The ideal soil pH for fruit plants ranges between 6.0 and 7.5. Conducting soil tests to assess pH and nutrient levels allows for necessary amendments, creating optimal conditions for growth. Healthy soil supports root development and overall plant vitality, making it a fundamental aspect of sapodilla cultivation.
-
Watering Practices: Consistent watering is vital, especially during dry periods. Mature sapodilla plants benefit from deeper, less frequent watering, which encourages robust growth. However, caution is necessary to avoid overwatering, as these plants are susceptible to root rot.
-
Pest Management: Staying vigilant against pests such as aphids and scale is important. Implementing integrated pest management strategies, including the use of natural predators and organic treatments, helps maintain plant health and resilience.
By addressing these challenges and implementing best practices, you can create an ideal environment within the sapodilla tree growing zone for your sapodilla tree to flourish.
Conclusion
Understanding the appropriate growing zone for sapodilla trees is vital for ensuring their successful cultivation. By identifying the right climate conditions, gardeners can create an environment that supports the growth of these tropical fruit trees, ultimately leading to a fruitful harvest. This process involves recognizing the USDA hardiness classifications and assessing local climate factors such as temperature, humidity, and rainfall.
Key insights covered in this guide include:
- The significance of temperature ranges for sapodilla trees
- The importance of maintaining adequate humidity and soil quality
- The necessity of proper spacing to maximize yield
Utilizing resources like the USDA Plant Hardiness Map and local gardening centers can greatly assist in determining the most suitable growing zone for these plants. Addressing challenges such as frost protection and pest management further enhances the chances of successful cultivation.
In conclusion, cultivating sapodilla trees requires careful consideration of various climatic factors and best practices tailored to specific growing zones. By taking the time to assess local conditions and implementing effective strategies, gardeners can enjoy the beauty and bounty of sapodilla trees. Embracing these practices contributes not only to a thriving garden but also fosters a deeper connection with the natural environment, encouraging sustainable gardening efforts.
Cultivate Your Own Tropical Paradise Today!
Start your journey with high-quality sapodilla trees from Everglades Farm and enjoy the fruits of your labor.
🛒 Explore sapodilla trees for sale
Frequently Asked Questions
What are growing zones and why are they important for sapodilla trees?
Growing zones are defined geographical areas that reflect specific climate conditions, particularly temperature ranges. They are important for sapodilla trees as they help determine if the local climate is suitable for planting, ensuring the plants thrive.
What USDA hardiness classifications are suitable for sapodilla trees?
Sapodilla trees flourish in USDA hardiness zones 9 to 11, where temperatures generally vary from 20°F to 30°F for Area 9, with slight frost.
How can I find my growing zone for sapodilla trees?
You can find your growing zone by consulting the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, which categorizes regions based on their average annual minimum temperatures.
How long does it take for sapodilla trees to produce fruit?
Sapodilla trees may take three or more years before producing a yield.
Do sapodilla trees require other plants for better yields?
Yes, while sapodilla trees are self-fertile, they tend to produce greater harvests when situated near other plants.
What advantages do tropical plants from Everglades Farm's Fast-Growing Trees collection offer?
These tropical plants are designed for rapid gardening success, allowing home gardeners to enjoy the benefits of high-yield species.
Why is selecting the right growing zone crucial for sapodilla trees?
Selecting the right growing zone is essential because it ensures that sapodilla trees receive the warmth and conditions necessary for optimal growth.

