Mastering Tamarind Tree Care: A Step-by-Step Guide
Share
Cultivating a tamarind tree can be a rewarding endeavor, particularly when considering its unique fruit and numerous culinary uses. Understanding the specific characteristics and growing conditions required for these tropical trees is essential for any aspiring gardener.
However, many face challenges in ensuring their tamarind trees thrive, from selecting the right soil to managing pests and diseases.
What steps can be taken to master the art of tamarind tree care and guarantee a bountiful harvest? This guide delves into the intricacies of tamarind cultivation, offering a comprehensive roadmap to successful growth and maintenance.
Grow a Tamarind Tree in your garden - explore fruit trees for sale.
1. Understand Tamarind Tree Characteristics and Growing Conditions
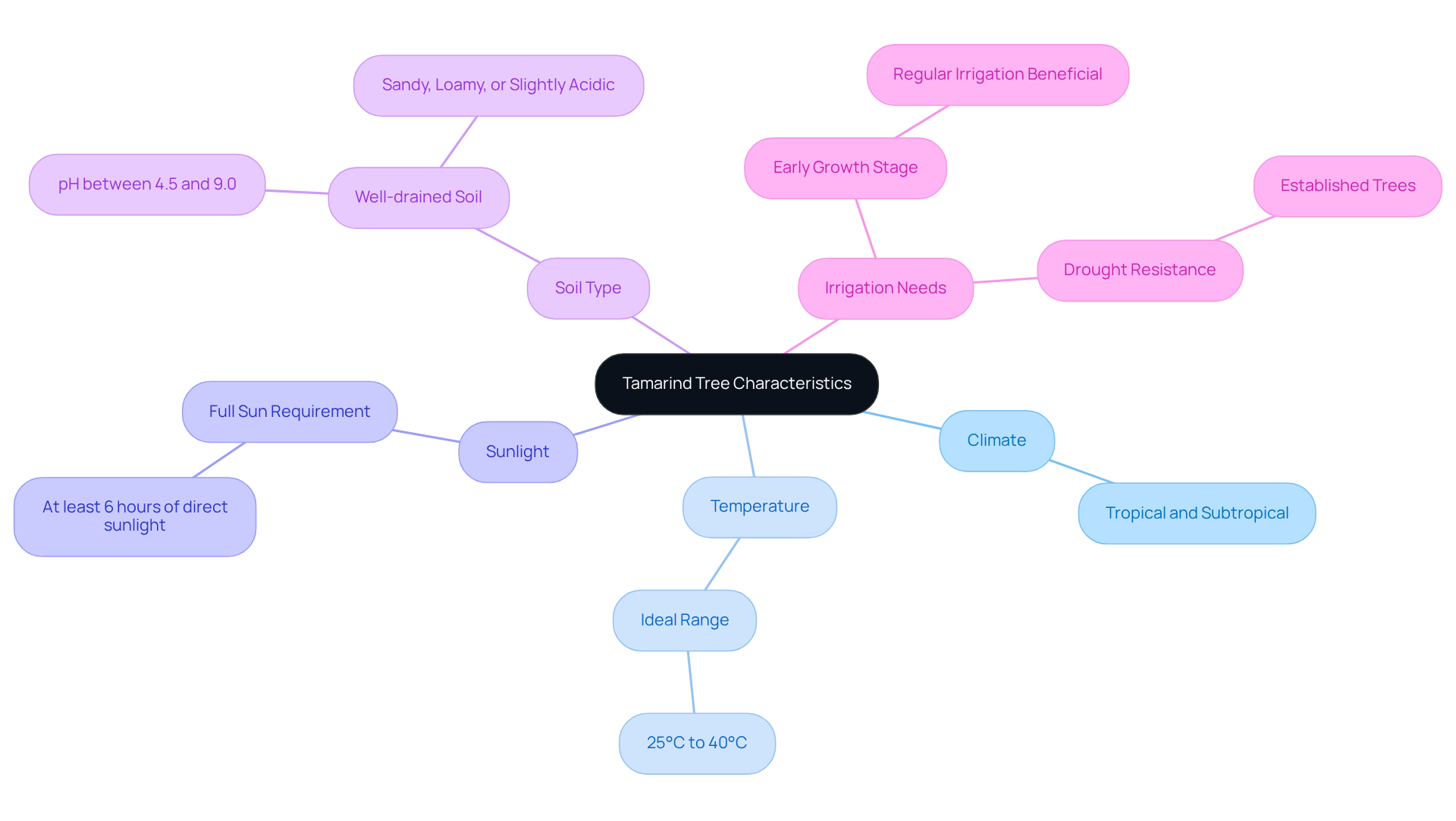
Tamarind trees (Tamarindus indica) are well-suited for tropical and subtropical climates, thriving best within a temperature range of 25°C to 40°C (77°F to 104°F). These plants require , needing at least six hours of direct sunlight each day. For optimal growth, they prefer well-drained soil with a pH between 4.5 and 9.0. Although tamarind plants exhibit drought resistance once established, they significantly benefit from regular irrigation during their early growth stages. Establishing an environment that meets these specific conditions is crucial for the successful cultivation of the tamarind tree, allowing it to flourish and produce its delicious, nutrient-rich pods.
2. Follow Step-by-Step Planting Instructions for Tamarind Trees
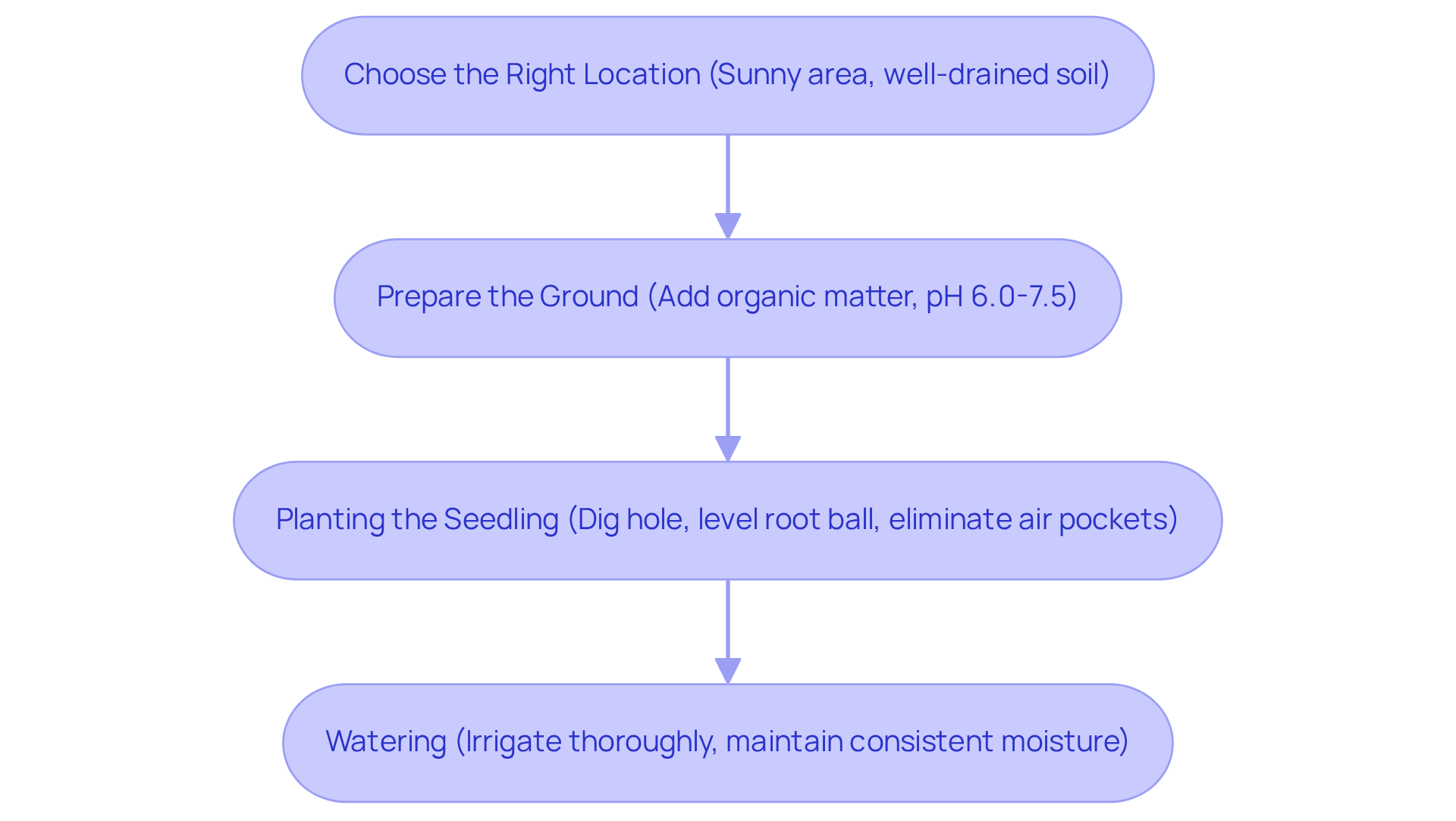
- Choose the Right Location: Selecting a sunny area with well-drained earth is crucial, as the tamarind tree thrives in full sunlight and requires good drainage to prevent root rot. It is essential to avoid locations prone to waterlogging, as excess moisture can hinder growth.
- Prepare the Ground: Enhance the earth by incorporating organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, to improve drainage and nutrient content. Research indicates that enhancing earth with organic materials can significantly boost the health and productivity of tropical trees. For instance, one ton of chicken manure can contribute approximately 21 kg of nitrogen (N), 12 kg of phosphorus (P), and 13 kg of potassium (K) to the ground, making it an excellent option for the growth of the tamarind tree. Aim for a pH between 6.0 and 7.5, which is ideal for the tamarind tree's growth.
- Planting the Seedling: Dig a hole that is twice the width and the same depth as the root ball of the seedling. Place the seedling in the hole, ensuring that the top of the root ball is level with the surrounding earth surface. Replenish the hole with earth, gently pressing down to eliminate air pockets that can hinder root establishment. Successful tamarind cultivators, such as Oscar Baluyot, have demonstrated that lead to healthier plants and improved yields.
- Watering: After planting, irrigate the tree thoroughly to assist in settling the ground around the roots. For the initial months, it is vital to maintain consistent moisture in the soil without allowing it to become soggy. Consistent watering is essential for developing a robust root system, particularly during the early stages of growth. According to Dr. Felomina Reyes, these plants typically begin producing fruit after 3-5 years, yielding between 2.9 to 12 kg per plant, underscoring the importance of proper care during the initial development phase.
By adhering to these best practices, you can ensure a successful start for your tamarind tree, which will help establish a strong foundation for healthy growth and fruitful yields.
3. Implement Care and Maintenance Practices for Healthy Growth
- Watering young tamarind trees is essential, as they require , ideally 2-3 times a week during their first year, particularly in dry conditions. It is crucial to check soil moisture prior to watering to prevent overwatering, which can lead to root rot. Once established, the tamarind tree can thrive on a weekly watering schedule, with adjustments based on seasonal changes and local climate conditions. In hotter climates, more frequent watering may be necessary to counteract increased evaporation.
- Fertilization: To ensure optimal development and fruit production, apply a balanced fertilizer, such as a 10-10-10 NPK mix, three times a year: early spring, mid-summer, and early fall. This schedule guarantees that the plants receive essential nutrients during their active growth stages. Regular monitoring of nutrient levels can help in adjusting fertilization strategies as needed, ensuring the plant effectively responds to the nutrients provided.
- Pruning: Trim the plants in late winter or early spring to remove any dead or diseased branches. This practice not only shapes the plant but also improves air circulation and sunlight penetration, promoting healthier growth and preventing the spread of disease.
- Mulching: Applying a layer of organic mulch around the base of the tamarind tree is beneficial for moisture retention and weed suppression. Ensure that the mulch does not touch the trunk to prevent rot, and consider using organic materials like compost or shredded bark for added nutrients.
4. Troubleshoot Common Problems in Tamarind Tree Cultivation
- Pest control is crucial because the tamarind tree is susceptible to pests such as mealybugs and aphids, which can significantly impact its health. Regular inspections are essential for the early detection of infestations. By applying neem oil or insecticidal soap, you can effectively manage these pests, fostering a healthier environment for the plants. Additionally, introducing beneficial insects like ladybugs can naturally help control aphid populations.
- The tamarind tree is known for its unique fruit. Disease Prevention: Root rot is a common issue for the tamarind tree, often resulting from waterlogged soil. To prevent this, ensure that your planting area has excellent drainage and avoid overwatering. Conducting routine ground assessments can help identify nutrient deficiencies that may render your plant more susceptible to diseases. Applying mulch around the base of the plant can also help retain moisture and prevent evaporation, further supporting healthy growth.
- Environmental Stress: Yellowing or dropping leaves may indicate , frequently associated with overwatering or insufficient sunlight. Adjust your watering schedule based on moisture levels and ensure your tamarind tree receives adequate light to thrive. Moreover, providing sufficient spacing between trees can improve air circulation, thereby reducing the risk of pest and disease occurrences.
- Fertilizer Burn: If you observe brown tips on the leaves, this may indicate over-fertilization. To remedy this, reduce the frequency of fertilizer applications and flush the soil with water to remove excess nutrients. A balanced slow-release fertilizer can help maintain optimal nutrient levels without the risk of burn. Be mindful that fruit drop can have economic implications for commercial growers, so monitoring for signs of stress is crucial.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of tamarind tree care requires a thorough understanding of the specific needs of these remarkable trees and the implementation of best practices for their growth. By focusing on the right climate, soil conditions, and care techniques, one can successfully cultivate a thriving tamarind tree that not only enhances the landscape but also produces delicious, nutrient-rich pods.
Key aspects of successful tamarind cultivation include:
- Selecting an ideal planting location
- Preparing the soil with organic matter
- Employing proper planting techniques
- Maintaining consistent watering and fertilization schedules
Furthermore, regular pruning, effective pest management, and proactive disease prevention are vital in ensuring the health and productivity of the tree. By adhering to these step-by-step instructions, growers can establish a solid foundation for their tamarind trees, leading to fruitful harvests.
Ultimately, the journey of tamarind tree cultivation is both rewarding and impactful. Engaging with these trees fosters an appreciation for their unique characteristics and contributes to sustainable practices in gardening and agriculture. By embracing the knowledge and techniques outlined in this guide, individuals can empower themselves to cultivate their own tamarind trees successfully, enriching their gardens and communities with the joys of this extraordinary plant.
Cultivate Your Own Tamarind Tree Today!
Unlock the secrets to thriving tamarind cultivation with Everglades Farm's premium plants and expert guidance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What climate is ideal for growing tamarind trees?
Tamarind trees thrive best in tropical and subtropical climates, with an optimal temperature range of 25°C to 40°C (77°F to 104°F).
How much sunlight do tamarind trees need?
Tamarind trees require full sun, needing at least six hours of direct sunlight each day for optimal growth.
What type of soil is best for tamarind trees?
Tamarind trees prefer well-drained soil with a pH between 4.5 and 9.0.
Are tamarind trees drought-resistant?
Yes, tamarind trees exhibit drought resistance once established, but they benefit significantly from regular irrigation during their early growth stages.
Why is it important to meet the specific growing conditions for tamarind trees?
Establishing an environment that meets the specific growing conditions is crucial for the successful cultivation of the tamarind tree, allowing it to flourish and produce its delicious, nutrient-rich pods.

