
Grow Your Ginger Plant: Essential Steps for Home Gardeners
Share
Ginger, a cherished spice celebrated for its culinary versatility and health benefits, necessitates specific conditions to thrive, making it an intriguing option for home gardeners. This guide outlines the essential steps for cultivating ginger, beginning with an understanding of its unique growing requirements and culminating in the mastery of harvesting techniques. Given its delicate needs and potential challenges, aspiring gardeners may wonder how to ensure a flourishing ginger plant that produces a bountiful harvest.
Want to grow a Ginger Plant in your garden?
Explore ginger plants for sale at Everglades Farm - shipped directly from Florida.
1. Understand Ginger's Growing Requirements
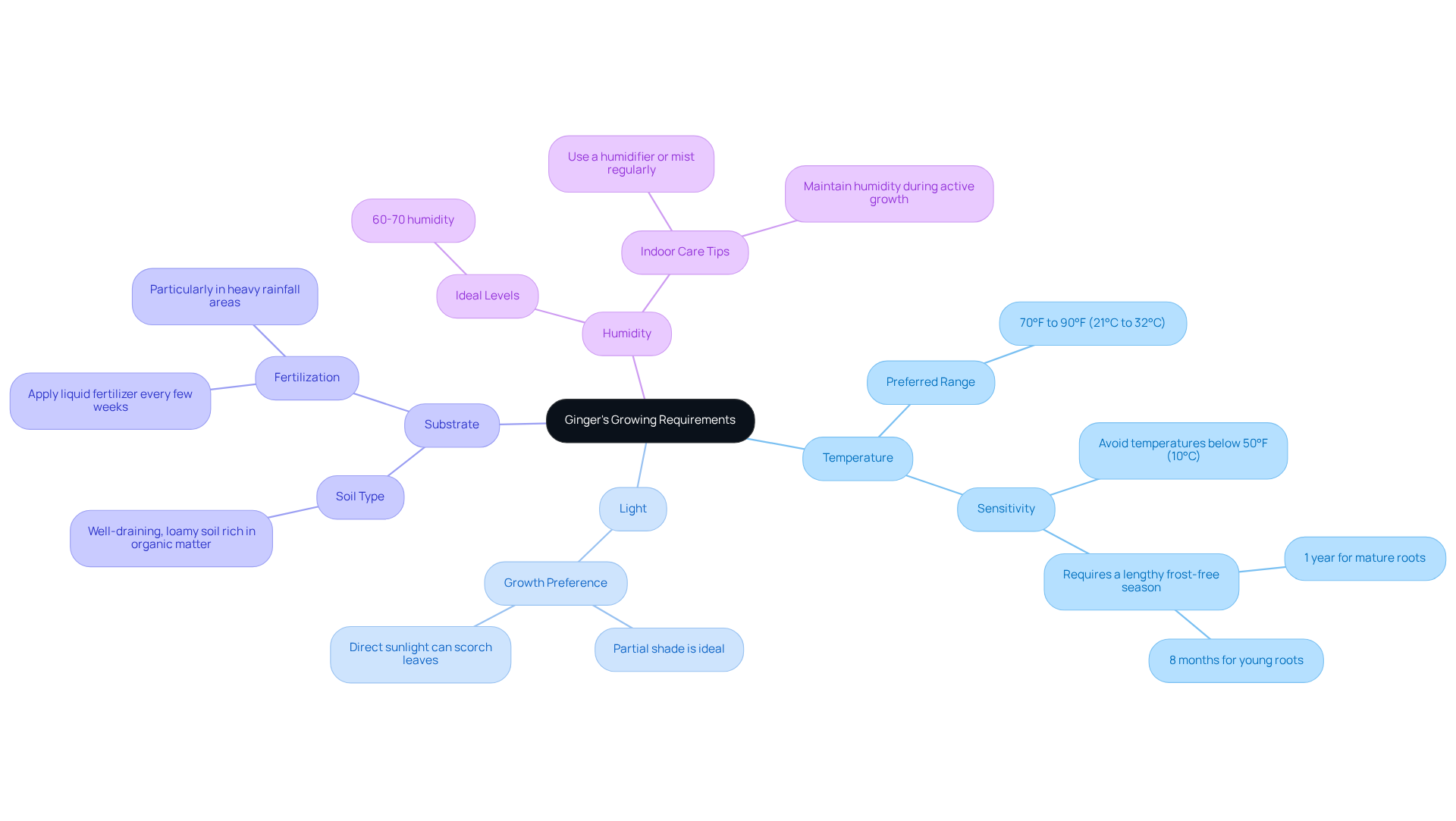
Ginger (Zingiber officinale) thrives in warm, humid conditions. Understanding its key requirements is essential for .
- Temperature: Ginger prefers temperatures ranging from 70°F to 90°F (21°C to 32°C). It is sensitive to cold and should not be exposed to temperatures below 50°F (10°C). Horticulturists emphasize that maintaining these temperatures is crucial for optimal growth. Moreover, ginger requires a lengthy frost-free growing season, approximately one year for mature roots and eight months for young roots, ensuring robust development.
- Light: This spice grows best in partial shade. Direct sunlight can scorch the leaves, making a location with filtered sunlight ideal for its growth.
- Substrate: A well-draining, loamy substrate rich in organic matter is recommended. The soil should retain moisture without becoming waterlogged, as the roots are susceptible to decay in saturated conditions. Additionally, applying liquid fertilizer every few weeks after planting is advised, particularly in regions with significant rainfall, to promote optimal growth.
- Humidity: High humidity levels, around 60-70%, are advantageous for ginger development. When cultivating indoors, consider using a humidifier or misting the foliage regularly. Maintaining these humidity levels is particularly important during active growth periods.
By ensuring these conditions are met, you can create an ideal environment for your ginger to thrive. Case studies indicate that cultivating this herb in warm regions, such as Virginia, yields delicious results when proper attention is given, including starting the growth indoors to secure the necessary warmth and moisture.
2. Plant Ginger: Step-by-Step Instructions
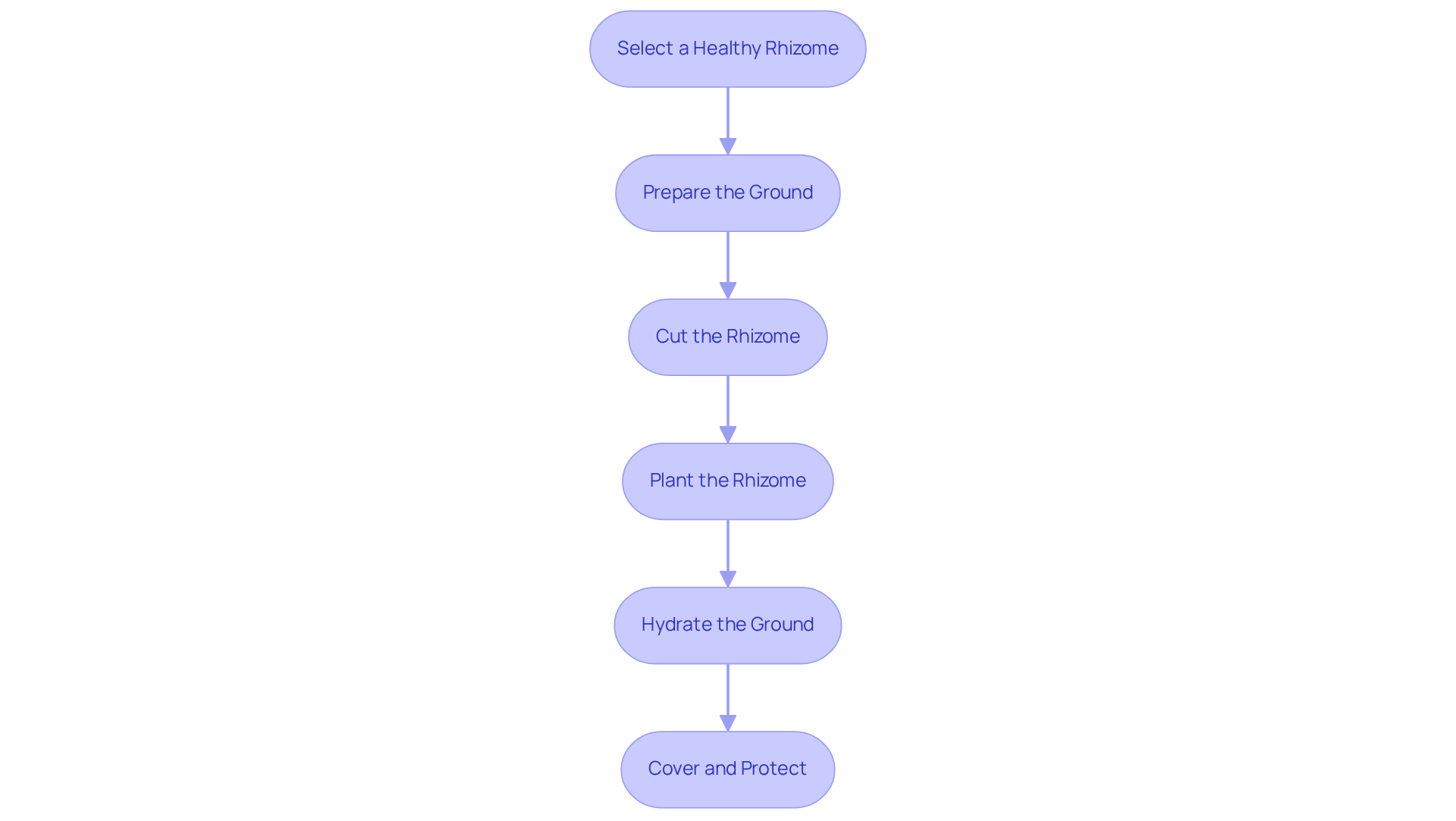
To successfully plant your ginger, follow these essential steps:
- Select a Healthy Rhizome: Choose a fresh ginger rhizome that has visible buds (eyes). It should be firm, light-colored, and free from mold or soft spots. Experts suggest selecting rhizomes of the ginger plant that are plump and possess multiple bumpy nodules for ideal development.
- Prepare the Ground: Create a nutrient-rich environment by mixing well-draining potting mix with compost. The ginger plant flourishes in slightly acidic earth with a pH between 5.5 and 6.5, so it is important to ensure the ground is loose and rich in organic matter to encourage healthy development.
- Cut the Rhizome: If your rhizome is large, cut it into smaller sections, ensuring each piece has at least one bud. Allow the cut pieces to dry for about a day to prevent rot, which is crucial for successful planting.
- Plant the Rhizome: Dig a hole approximately 2-4 inches deep in the prepared earth. Place the rhizome pieces with the buds facing up, spacing them about 6-8 inches apart if planting multiple pieces. This spacing allows for adequate growth and air circulation.
- After planting the ginger plant, hydrate the ground adequately to settle it around the rhizomes. Maintain consistent moisture, ensuring the ground remains moist but not soggy, as ginger prefers well-drained conditions.
- Cover and Protect: If planting outdoors, cover the area with mulch to retain moisture and regulate soil temperature. For indoor planting, position the pot in a warm, bright location, ideally maintaining temperatures between 68-86°F (20-30°C) while avoiding direct sunlight. The ginger plant requires 2-5 hours of direct daily sunlight and for optimal development.
By following these steps, you will create a solid base for your herb's growth, preparing for a bountiful harvest in approximately 8-10 months.
3. Care for Your Ginger Plant: Maintenance Tips
To ensure your ginger plant thrives, it is essential to follow these maintenance tips:
- Watering: Maintain consistently moist soil, particularly during the growing season. Water deeply once a week, allowing the to dry out between waterings. Frequent watering is crucial during active development phases, but avoid excessive watering, as this plant does not tolerate damp conditions. Appropriate watering methods help sustain ideal conditions for the plant, preventing root rot and encouraging robust rhizome development.
- Fertilizing: Apply a balanced, slow-release fertilizer every 4-6 weeks during the growing season. Organic alternatives, such as compost or fish emulsion, are effective and can enhance productivity. Magnesium is vital for photosynthesis, enzyme activation, and root growth in ginger species, making it an essential element of your fertilization strategy. Additionally, phosphorus is particularly important for energy transfer and root development, fostering robust growth.
- Pest Management: Regularly inspect for pests such as aphids and spider mites. If infestations occur, use neem oil or insecticidal soap as natural remedies. Effective pest control strategies are crucial for maintaining vegetation health and yield.
- Pruning: Remove any yellowing or dead leaves to promote airflow and prevent disease. This practice encourages new growth and helps sustain the overall vitality of the organism.
- Temperature Control: If growing indoors, ensure the plant is kept in a warm environment, ideally around 75°F (24°C). Avoid positioning it near drafts or air conditioning vents, as this plant flourishes in warm conditions and can be harmed by cold temperatures. Remember, this spice requires a lengthy, warm growing period of approximately 10 months to thrive.
By following these care tips, you can cultivate a healthy ginger plant, which will lead to a plentiful harvest.
4. Harvest Ginger: Timing and Techniques
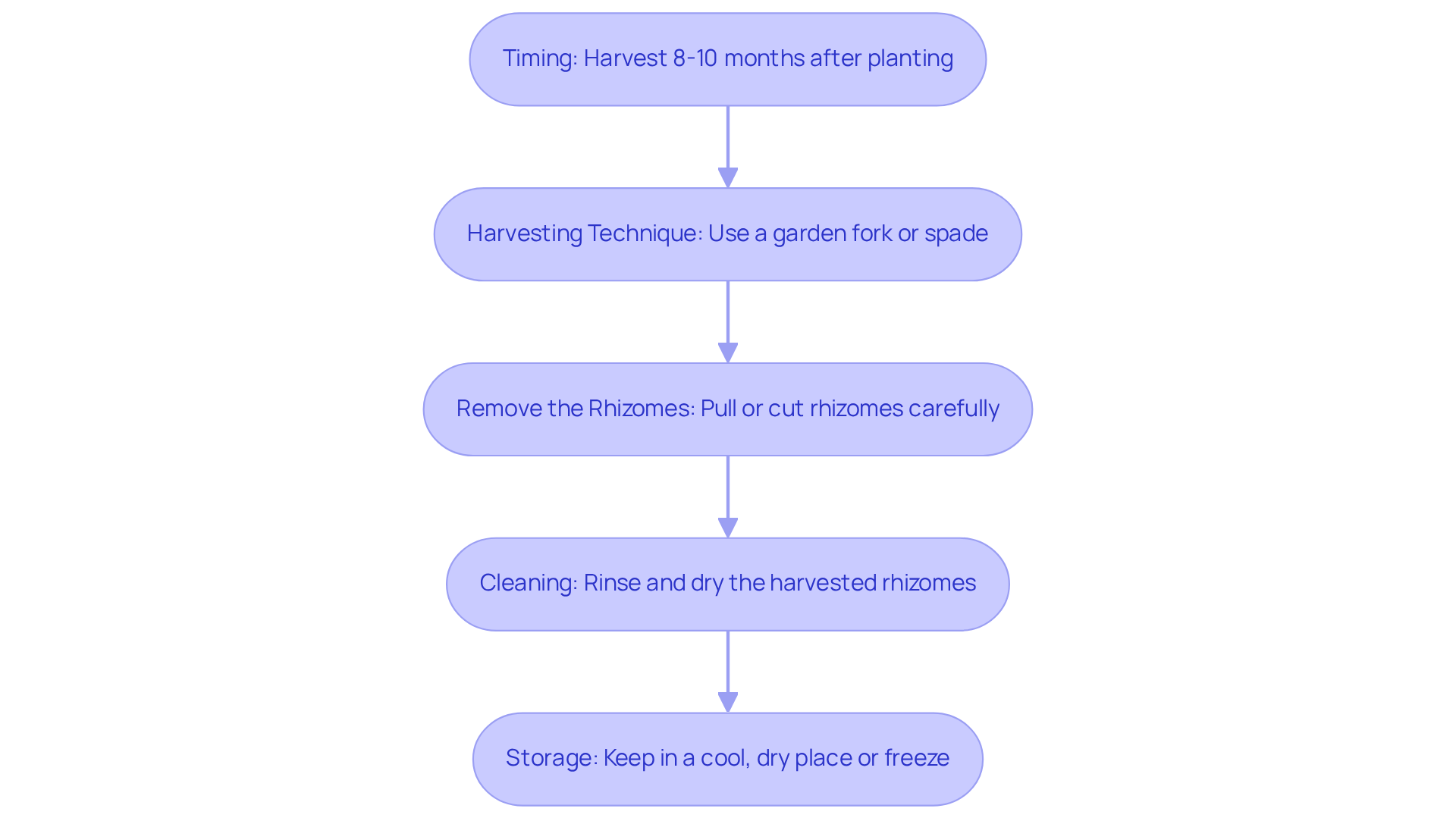
To successfully harvest your ginger, follow these essential steps:
- Timing: Ginger is typically ready for harvest 8 to 10 months after planting, as indicated by yellowing leaves and dying stems. For younger roots, harvesting can begin as early as 4 months, allowing for a milder flavor. Research indicates that a healthy ginger plant can produce roughly 1 to 2 pounds of rhizomes per plant, depending on growing conditions.
- Harvesting Technique: Use a garden fork or spade to gently loosen the earth around the vegetation, taking care not to damage the rhizomes. This technique minimizes the risk of injury to the roots, ensuring a healthier harvest. Experienced gardener Lisa Munniksma advises, "Be gentle when harvesting; the rhizomes are delicate and can be easily damaged."
- Remove the Rhizomes: Carefully pull the specimen from the soil to expose the rhizomes. You can choose to or selectively cut off a portion of the rhizome, which allows the plant to continue growing. A case study on effective harvesting methods for the spice emphasizes that leaving some rhizomes in the soil can encourage ongoing development for the following season.
- Cleaning: Rinse the harvested root under cool water to remove any soil residue. Allow it to dry completely before storing to prevent mold growth. It's important to handle the rhizomes gently during this process to avoid bruising.
- Storage: Keep fresh root in a cool, dry location. For extended preservation, consider freezing or drying the rhizomes, which can enhance their usability in cooking. Proper storage methods can significantly prolong the shelf life of your root, with frozen varieties lasting up to 6 months.
By adhering to these harvesting techniques and incorporating best practices, you can maximize your yield and enjoy the vibrant flavors of fresh ginger in your culinary creations.
Conclusion
Ginger cultivation presents a rewarding opportunity that necessitates an understanding of its unique growing conditions and care requirements. By establishing an environment that emphasizes warmth, humidity, and appropriate soil conditions, home gardeners can effectively grow this flavorful spice. The essential steps outlined in the article—from selecting healthy rhizomes to the meticulous harvesting of mature roots—offer a comprehensive guide for anyone interested in cultivating ginger at home.
Key insights highlight the necessity of maintaining optimal temperatures, ensuring adequate moisture without the risk of overwatering, and implementing effective pest management strategies. Furthermore, the article underscores the importance of timing in both planting and harvesting to maximize yield and flavor. Adhering to these guidelines not only enhances the growth of the ginger plant but also fosters a sustainable gardening practice.
Ultimately, growing ginger at home unlocks a realm of culinary possibilities while nurturing a deeper connection to the gardening process. By taking proactive steps and applying the discussed tips, anyone can relish the satisfaction of nurturing their own ginger plants, culminating in a bountiful harvest that enriches meals with fresh, aromatic flavor. Embrace the journey of ginger cultivation and savor the rewards it brings to your kitchen.
Cultivate Your Culinary Garden with Fresh Ginger!
Start your journey today and enjoy the flavorful rewards of home gardening with Everglades Farm.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the ideal temperature conditions for growing ginger?
Ginger thrives in temperatures ranging from 70°F to 90°F (21°C to 32°C) and should not be exposed to temperatures below 50°F (10°C).
How long does ginger need to grow before harvesting?
Ginger requires a lengthy frost-free growing season, approximately one year for mature roots and eight months for young roots.
What type of light is best for ginger cultivation?
Ginger grows best in partial shade, as direct sunlight can scorch its leaves. A location with filtered sunlight is ideal.
What substrate is recommended for growing ginger?
A well-draining, loamy substrate rich in organic matter is recommended. The soil should retain moisture without becoming waterlogged.
How often should fertilizer be applied when growing ginger?
It is advised to apply liquid fertilizer every few weeks after planting, especially in regions with significant rainfall.
What humidity levels are optimal for growing ginger?
High humidity levels around 60-70% are advantageous for ginger development.
How can humidity be maintained when growing ginger indoors?
When cultivating indoors, using a humidifier or misting the foliage regularly can help maintain the necessary humidity levels.
Can ginger be successfully grown in regions like Virginia?
Yes, cultivating ginger in warm regions such as Virginia can yield delicious results when proper attention is given, including starting the growth indoors to secure warmth and moisture.


