Cultivating an Azadi pomegranate tree can be a rewarding endeavor, offering vibrant fruit and serving as a stunning addition to any garden. Understanding the specific conditions these trees require is crucial for success, as factors such as soil type, sunlight, and proper care play significant roles in their growth. However, many aspiring gardeners encounter challenges like overwatering or pest infestations that can jeopardize their efforts. Navigating these potential pitfalls is essential to ensure a thriving Azadi pomegranate tree. This guide outlines four essential steps to successfully cultivate these beautiful trees, unlocking the secrets to fruitful growth.
Thinking about growing a Pomegranate Tree in your garden?
Explore Azadi Pomegranate Tree at Everglades Farm - shipped directly from Florida.

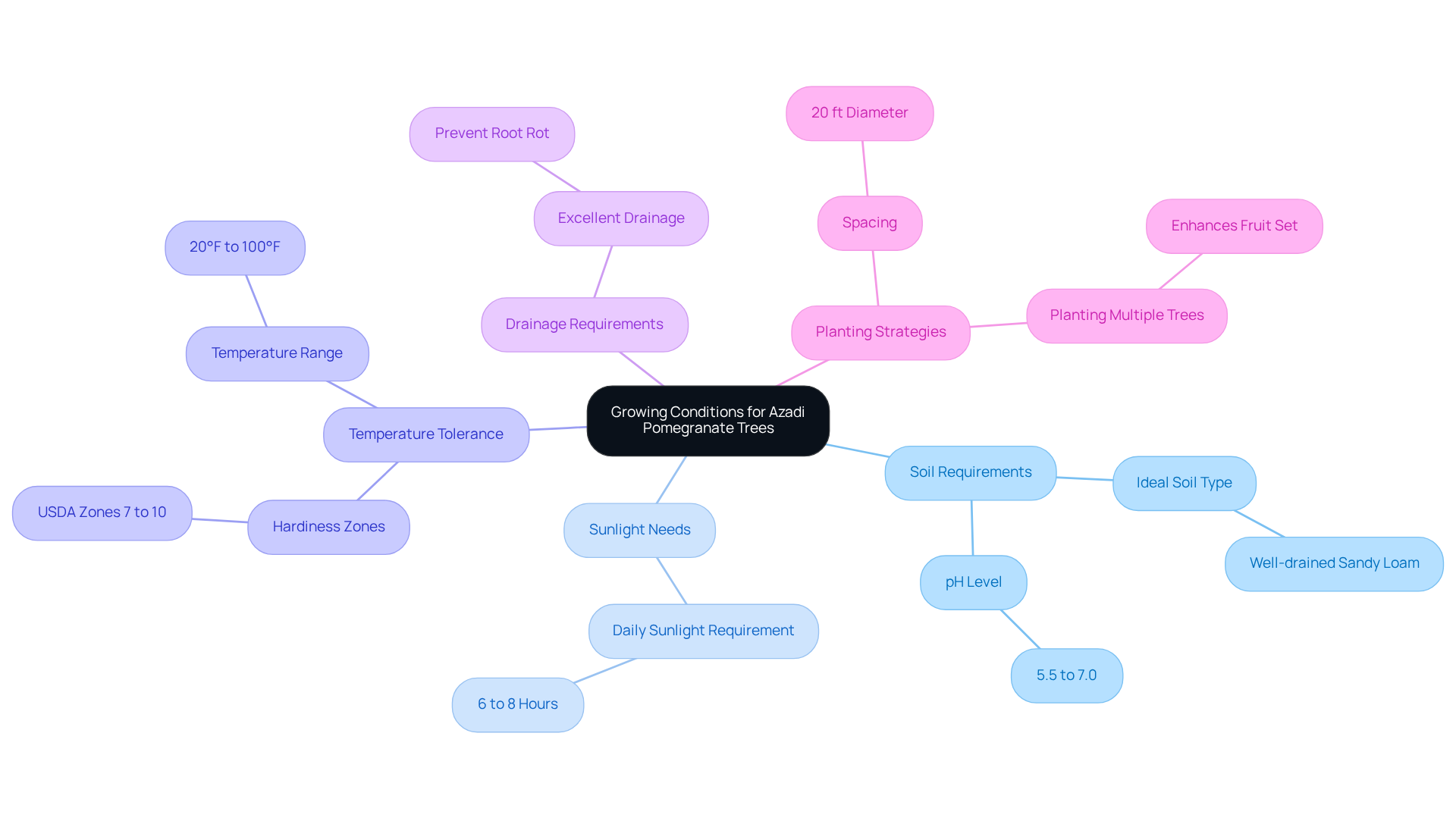
1. Understand the Growing Conditions for Azadi Pomegranate Trees
Azadi pomegranate trees thrive in
well-drained sandy loam, ideally with a pH between 5.5 and 7.0. This specific soil variety facilitates their growth and yield, as it allows for sufficient drainage while retaining essential moisture. The azadi pomegranate tree flourishes in full sun, requiring at least 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight daily to achieve optimal health and yield. Horticulturists emphasize that
adequate sunlight is crucial for maximizing fruit production. Hardy in USDA zones 7 to 10, the azadi pomegranate tree can withstand a wide temperature range, from 20°F to 100°F.
To prevent root rot, it is vital to select a planting location with
excellent drainage since these plants are sensitive to waterlogged conditions. Understanding local climate variations will also aid in providing for your plants, ensuring their long-term success. Additionally, planting two or more
fruit-bearing plants can enhance fruit set, which is advantageous for gardeners aiming to maximize their harvest. For optimal growth, ensure that the plants are spaced with a 20 ft diameter around each specimen.
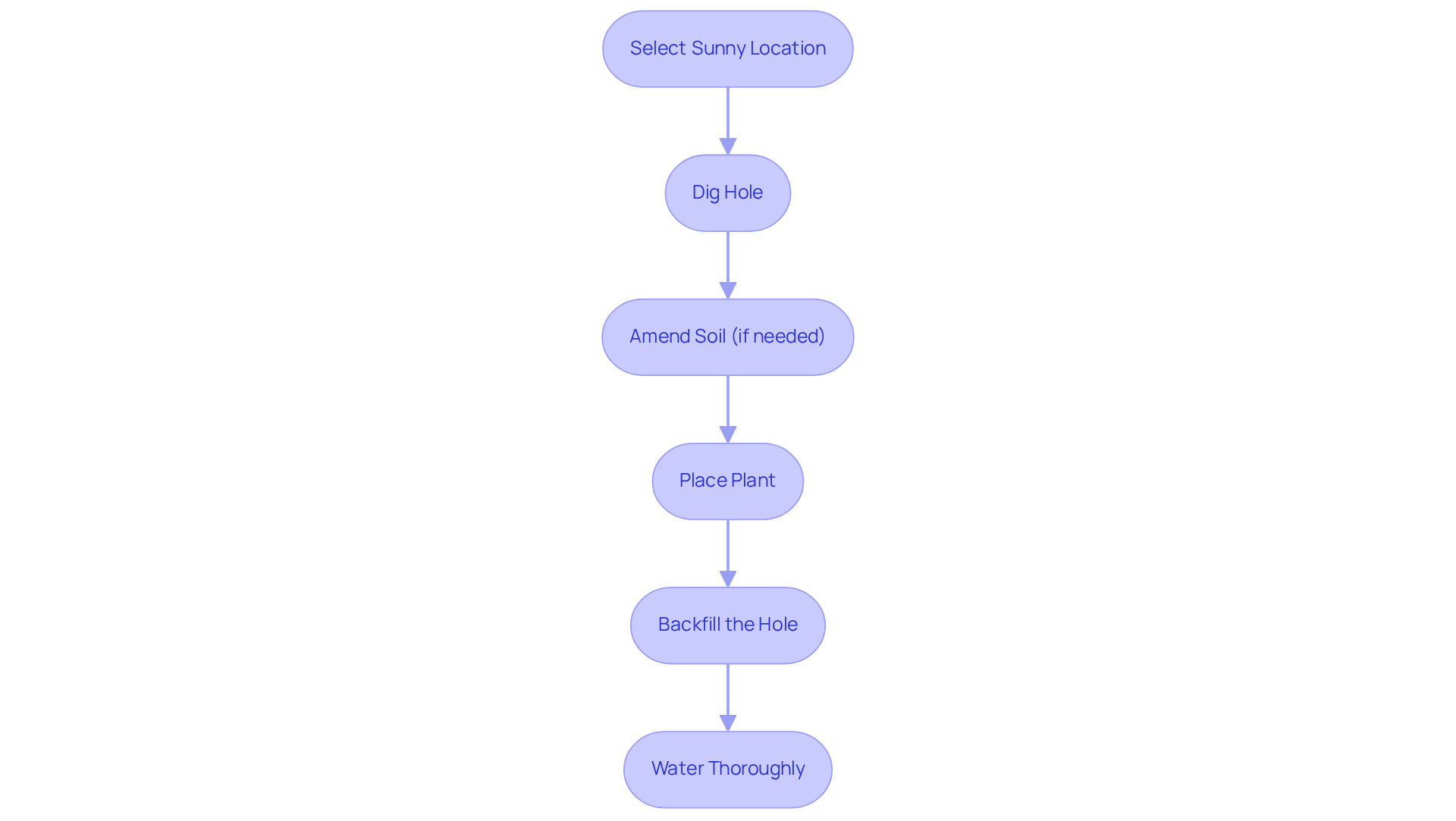
2. Plant the Azadi Pomegranate Tree Correctly
To successfully plant your Azadi pomegranate, begin by selecting a . The azadi
pomegranate tree thrives in full sunlight and requires
superior drainage for optimal growth. Pomegranates prefer soil with a pH of 6.0 to 7.0.
- Dig a hole that is twice as wide and equally deep as the root ball of the plant.
- If your soil is heavy clay, amend it with organic matter to improve drainage and encourage healthy root development.
- Place the plant in the hole, ensuring that the top of the root ball is level with the surrounding soil surface.
- Carefully backfill the hole with soil, gently tamping it down to remove any air pockets.
- After planting, water the plant thoroughly to help settle the soil around the roots, which is crucial for establishing a strong foundation.
Following these steps can significantly enhance your
planting success, as proper techniques are essential for the healthy development of the azadi pomegranate tree.
According to expert Andy Wilcox, applying a generous 2 to 3-inch layer of compost in the spring as the plants leaf out can further
boost growth and yield.
3. Maintain and Care for Your Azadi Pomegranate Tree
To ensure the health and productivity of your azadi pomegranate tree, is crucial. Begin by watering deeply but infrequently, allowing the soil to dry out between waterings to prevent root rot. During the growing season, apply a
balanced fertilizer with an N-P-K ratio of 10-10-10 or 14-14-14 in early spring, using approximately 1 to 2 pounds per tree, depending on its size. Agronomists advise against
high-nitrogen fertilizers to avoid excessive leaf growth that compromises yield. Consistent watering is particularly important during dry periods or while the produce is maturing. Additionally, ensure the
soil pH remains between 5.5 and 7.0 for optimal plant health.
Annual pruning is essential; remove any dead or overcrowded branches to enhance air circulation and promote healthy
fruit production. Keep a vigilant eye for
pests and diseases, such as aphids and fungal infections, and address any issues promptly to maintain the plant's vitality. As agronomists emphasize, appropriate fertilization and maintenance techniques are vital for optimizing yield and ensuring the long-term prosperity of the azadi pomegranate tree.
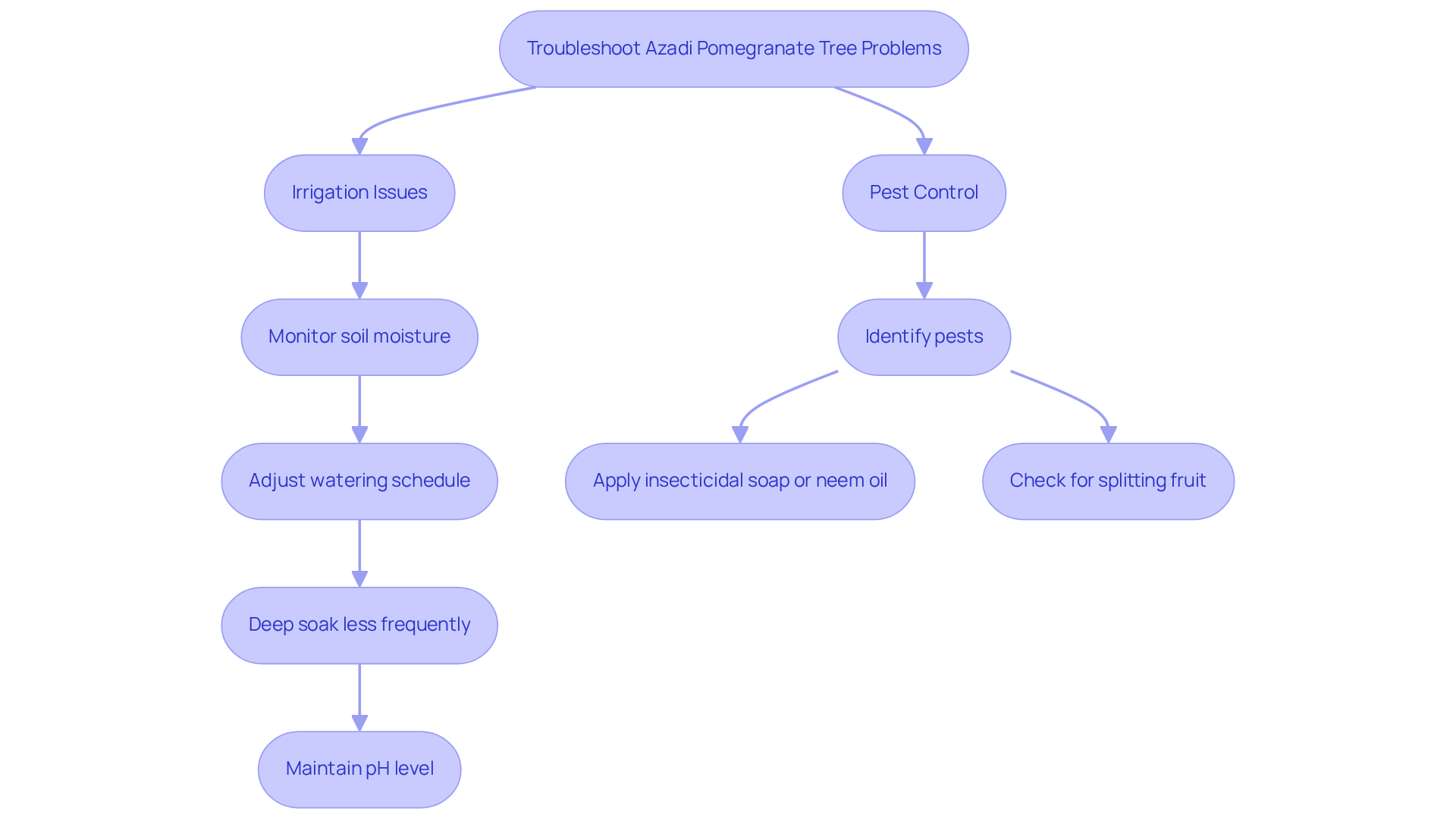
4. Troubleshoot Common Problems in Growing Azadi Pomegranate Trees
Cultivating the Azadi pomegranate tree presents several challenges, particularly in the areas of irrigation and pest control. One significant issue is
excessive watering, which can lead to root rot, severely affecting plant health. To mitigate this risk, it is essential to regularly and adjust your watering schedule to achieve consistent dampness without waterlogging the roots. As Brent Wilson emphasizes, deep soaking less frequently is far more beneficial than providing a small amount of water daily. Conversely, under-watering can result in wilting and leaf drop, making it crucial to find the right balance. Pomegranate plants thrive in a soil pH range of 5.5 to 7.2, which is vital for their overall health and productivity.
Pests such as aphids and mealybugs also threaten your azadi pomegranate tree. Effective management strategies include the application of
insecticidal soap or neem oil to control infestations. Furthermore, if you observe splitting fruit, it may be attributed to inconsistent watering or excessive rainfall. Brent Wilson notes that the goal is to maintain even soil moisture throughout the fall season, similar to the summer conditions—not too wet or too dry. To address this concern, ensure your azadi pomegranate tree receives steady moisture during its growing season, which is essential for the fruit development and overall vitality of the azadi pomegranate tree.
Conclusion
Successfully cultivating an Azadi pomegranate tree necessitates a comprehensive understanding of its specific requirements, ranging from soil selection to the mastery of care techniques. By concentrating on optimal growing conditions, meticulous planting, consistent maintenance, and effective problem-solving strategies, gardeners can ensure a thriving and productive tree that yields abundant harvests.
Key steps include:
- Ensuring well-drained, nutrient-rich soil with the appropriate pH.
- Employing planting techniques that foster healthy root development.
- Maintaining a careful balance of watering and fertilization.
Furthermore, recognizing and addressing common challenges such as pest control and irrigation issues is crucial for sustaining the tree's health and productivity.
Ultimately, the journey of growing an Azadi pomegranate tree transcends the mere production of fruit; it encompasses the enriching learning and gardening experience it provides. By applying the tips and techniques outlined, gardeners can cultivate a vibrant tree that not only enhances their landscape but also offers delicious and nutritious pomegranates. Embrace the process, and relish the rewards of nurturing this remarkable fruit tree.
Grow Your Own Azadi Pomegranate Today!
Start your gardening adventure with
Everglades Farm and enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious fruit.
🛒 Buy Azadi Pomegranate Tree
👉🏻 Explore Pomegranate Trees Collection for sale
Frequently Asked Questions
What type of soil is best for Azadi pomegranate trees?
Azadi pomegranate trees thrive in well-drained sandy loam, ideally with a pH between 5.5 and 7.0.
How much sunlight do Azadi pomegranate trees need?
They require at least 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight daily for optimal health and yield.
What USDA zones are suitable for growing Azadi pomegranate trees?
Azadi pomegranate trees are hardy in USDA zones 7 to 10.
What temperature range can Azadi pomegranate trees tolerate?
They can withstand a wide temperature range, from 20°F to 100°F.
Why is drainage important for Azadi pomegranate trees?
Good drainage is vital to prevent root rot, as these plants are sensitive to waterlogged conditions.
How can planting multiple Azadi pomegranate trees benefit fruit production?
Planting two or more fruit-bearing plants can enhance fruit set, maximizing the harvest.
What is the recommended spacing for planting Azadi pomegranate trees?
The plants should be spaced with a 20 ft diameter around each specimen for optimal growth.





0 comments